The Complete Guide to Becoming a Cyber Security Consultant
Unlock your new future as a cyber security consultant! Learn skills, certifications, and strategies to upskill, grow your career, and thrive in the digital era.

A recent industry-backed study has revealed a significant skills gap in India’s cybersecurity sector. Currently, the country has fewer than half of the 1 million cybersecurity professionals needed to meet the rising demand. This gap is primarily driven by the rapid growth of digital services, increased cloud usage, and the escalation of cyber threats, which necessitate strong defense teams in both government agencies and businesses.
Cybersecurity consulting, which uses cutting-edge solutions to prevent attacks and save companies time, money, and reputation, is perfect if you enjoy problem-solving, working with technology, and safeguarding enterprises from cyber threats.
This guide is designed for:
-
IT professionals looking to specialize.
-
Career changers seeking a high-demand tech career.
-
Students interested in cybersecurity.
This is not just a theoretical guide. It serves as a guide for advancing your career, developing new skills, and preparing yourself for the future. We'll show how platforms like Skillfloor can help you go more quickly from learner to certified consultant along the route.
Why Cyber Security Consulting Is the Career of the Future
To be honest, the field of cyber security is both exciting and concerning. Each year:
-
Over 4.5 billion records are compromised globally.
-
Cybercrime damages are projected to exceed $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
-
Businesses struggle to find qualified security experts, creating a massive talent gap.
This is your chance. Businesses are searching for reliable consultants who can safeguard their resources and future, not just workers. Cyber security consultancy is calling your name if you want a job where your skills are valued and you can have an immediate impact.
Understanding Cybersecurity Consulting
Before delving into technical expertise and credentials, it's critical to comprehend the true duties of a cybersecurity consultant.
What is a Cybersecurity Consultant?
A cybersecurity consultant is an expert who advises organizations on how to protect their digital assets. They identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, implement security measures, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Key Responsibilities
-
To find vulnerabilities, carry out comprehensive risk assessments and security audits.
-
Create and carry out efficient security plans, guidelines, and practices.
-
Use penetration testing to find and address system flaws.
-
Provide guidance to companies regarding regulatory compliance standards (such as GDPR and HIPAA) while highlighting the importance of cybersecurity in safeguarding vital data.
-
Keep an eye out for security issues and breaches and act quickly to address them.
-
Provide suggestions on how to lower risks and strengthen overall cybersecurity posture.
Types of Cybersecurity Consulting
-
Advisory Consulting: Advisory experts assist companies in identifying threats and developing efficient cybersecurity plans for long-term safety by offering guidance on overall security strategy, risk management, and policies.
-
Technical Consulting: Technical consultants concentrate on practical activities such as vulnerability assessments, system hardening, and penetration testing to find and address security flaws in digital infrastructure.
-
Compliance Consulting: In order to lower the risk of fines and preserve stakeholder and customer trust, compliance consultants make sure companies adhere to legal and regulatory regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
In-House Security Roles vs. Consulting Roles: Key Differences
-
In-House Security Roles: Work full-time for a single company and concentrate on safeguarding its networks, data, and systems. Maintaining long-term internal security procedures is part of the continuous, company-specific responsibilities.
-
Consulting Roles: Conduct audits, risk analyses, and compliance inspections for several clients in various industries. Here, a cyber security consultant can advise companies on cybersecurity best practices by bringing their knowledge, effective communication skills, and flexibility.
-
Key Difference: In-house positions concentrate on the ongoing security requirements of a single company, whereas consultancy positions offer diversity, exposure, and chances to address certain problems across several businesses.
Key Skills Every Cyber Security Consultant Should Have
The reality? Many would-be consultants freeze because they are unsure of where to begin. Although the field is large, it is manageable when it is divided into several categories.
Technical Skills
-
Networking Protocols: A cyber security consultant can detect vulnerabilities and successfully safeguard system communication by having a solid understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, and HTTP/HTTPS.
-
Operating Systems: Understanding Windows, Linux, and macOS enables consultants to effectively troubleshoot system-specific security concerns and safeguard a variety of settings.
-
Cloud Platforms: Data protection and secure cloud infrastructure management are made easier with an understanding of AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and cloud security concepts.
-
Security Tools: Proactive monitoring, threat identification, and security risk reduction are made possible by the use of SIEM systems, IDS/IPS, and vulnerability scanners.
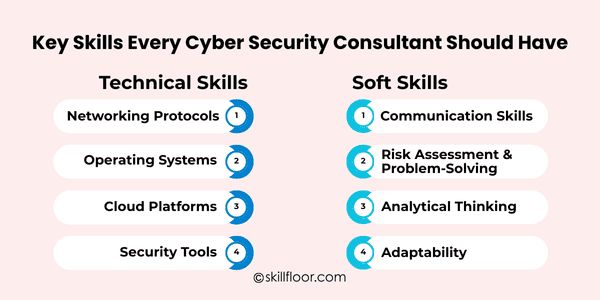
Soft Skills
-
Communication Skills: Consultants may help clients understand complicated threats to cybersecurity through clear communication, which facilitates well-informed decision-making and appropriate security implementation.
-
Risk Assessment & Problem-Solving: The capacity to evaluate risks and create remedies guarantees that vulnerabilities are found and fixed before they cause serious harm.
-
Analytical Thinking: Analytical abilities enable consultants to spot trends, identify possible dangers, and react fast to changing cybersecurity issues.
-
Adaptability: To offer efficient security solutions, a cyber security consultant must quickly adjust to new threats, technologies, and client environments.
Tip: Soft skills are frequently what set a decent consultant apart from an excellent one. A detailed explanation of technical concerns is highly valued by clients.
Educational Pathways
Although a computer science degree is not required to work as a cybersecurity consultant, formal education can be beneficial.
1. Degree Options
-
Bachelors in Computer Science, Information Security, or Cybersecurity.
-
Master’s degrees in Cybersecurity or Information Assurance (for advanced positions).
2. Certifications
Certifications increase your marketability as a cyber security consultant and attest to your expertise:
-
Entry-level: CompTIA Security+, CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker), and CEHP (Certified Ethical Hacking Professional) help you build foundational ethical hacking skills.
-
Mid-level: CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional), CISM provides in-depth knowledge of information security management and governance.
-
Specialized: OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional), CCSP (Certified Cloud Security Professional) focus on advanced penetration testing and cloud security expertise.
3. Other Learning Options
-
Online Courses and Bootcamps: Enroll in online boot camps or courses, such as those provided by Skillfloor, to acquire useful cybersecurity skills fast.
-
Hands-On Labs and Virtual Environments: Practice in virtual and simulated labs to improve technical expertise and practical problem-solving skills.
-
Self-Study: Use cybersecurity communities, books, and tutorials to remain current with trends, learn new things, and explore new subjects.
How to Gain Hands-On Experience as Cybersecurity Consultant
Real-world experience is essential. Here’s how to get it:
-
Internships and Apprenticeships: Learn practical problem-solving approaches and get real-world skills by working with seasoned cybersecurity specialists.
-
Home Labs: To effectively practice hacking, monitoring, system security, and testing security technologies, set up virtual machines.
-
CTFs (Capture the Flag Challenges): Take part in gamified cybersecurity workouts to hone your abilities, mimic assaults, and pick up new capabilities.
-
Bug Bounty Programs: Find weaknesses in operational systems to earn rewards and advance your knowledge of ethical hacking.
-
Open-Source Contributions: Participate in security-focused open-source projects to network, discover best practices, and demonstrate real-world cybersecurity expertise.
-
Workshops and Training Sessions: Participate in practical workshops to apply your knowledge in real-world situations and network with professionals in the field.
Tip: Candidates with actual, practical cybersecurity skills are preferred by employers and clients since practical abilities are frequently more important than academic understanding.
Building Your Personal Brand
In consulting, your reputation matters as much as your technical skills.
-
Professional LinkedIn Profile: Emphasize your experience, projects, and certificates to demonstrate your skills and draw in clients or employers.
-
Content Creation: Create a GitHub repository, YouTube channel, or blog to spread knowledge and exhibit thought leadership.
-
Networking Events: Attend cybersecurity gatherings and conferences to network with business leaders and possible customers.
-
Professional Organizations: For networking and educational possibilities, join local cybersecurity communities or organizations like (ISC)² ISACA.
-
Public Speaking: Give presentations at events, workshops, or webinars to build your reputation and visibility in the cybersecurity industry.
-
Mentorship: Assist peers or novices in cybersecurity, which improves your standing and fosters business connections.
Understanding the Business Side
Consulting isn’t just about technical expertise; it’s also a business.
-
Client Acquisition: Establishing trust is essential. To get new clients, start with little jobs, referrals, and networking.
-
Pricing Models: Depending on the needs of the client and the complexity of the project, choose between hourly, retainer-based, or project-based charging.
-
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Always observe rules, regulations, and Ethics in Cyber Security to protect yourself and keep client trust.
-
Contracts and Agreements: To prevent disagreements, clearly describe the project's scope, deliverables, deadlines, and roles in written agreements.
-
Marketing Your Services: Reach potential customers by promoting your knowledge on websites, social media, and professional networks.
-
Client Communication: To establish solid, enduring client connections, communicate in a timely, professional, and transparent manner.
Tip: You may differentiate yourself and gain the trust of clients and decision-makers by effectively conveying cybersecurity threats and solutions in plain commercial terms.
Tools & Technologies Every Consultant Should Know
-
Penetration Testing: Nmap, Burp Suite, and Metasploit aid in finding weaknesses and testing system security.
-
Vulnerability Assessment: Nessus OpenVAS identifies vulnerabilities and offers useful reports for fixing them.
-
Security Monitoring & Reporting: SIEM systems, such as ELK stack and Splunk, monitor, evaluate, and notify users of questionable activities.
-
Compliance Auditing: Legal and regulatory compliance is ensured by GDPR, ISO 27001, and HIPAA assessment tools.
-
Endpoint Security Tools: Devices are protected and malware breaches are avoided by antivirus and EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) software.
-
Network Traffic Analysis Tools: Network communications can be monitored, troubleshooted, and secured with the aid of programs like tcpdump and Wireshark.
Challenges a Cyber Security Consultant May Face
-
Rapidly Evolving Threats: It takes ongoing education and alertness to stay current with emerging malware, cyberthreats, and attack methods.
-
Managing Client Expectations: In consulting assignments, it can be difficult to strike a balance between high-pressure circumstances, client demands, and practical security objectives.
-
Long Working Hours: Extended or erratic working hours are frequently necessary for responding to security issues, audits, or urgent breaches.
-
Maintaining Certifications: Maintaining credibility and competitiveness in the field requires regular updating and renewal of professional certificates.
-
High Responsibility: Since consultants are responsible for the protection of client data, errors could have detrimental effects on their reputation or finances.
-
Continuous Learning: The rapidly evolving field of cybersecurity necessitates ongoing skill development as well as adjustment to new tools, technology, and laws.
Tip: You can keep ahead of new risks and take advantage of greater career opportunities by being proactive in cybersecurity through ongoing education, skill development, and networking.
Becoming a cyber security consultant offers a unique opportunity to make a significant impact in the digital world; it can be more than just a career. Every system you protect, every threat you prevent, and every company you advise adds value and builds trust. Although the journey may initially seem daunting, you can transform your ambition into achievement by taking it step by step—learning new skills, gaining practical experience, and obtaining certifications. Remember, you are in control of your own development. Resources like Skillfloor can support your learning, practice, and success. If you remain persistent and curious, you can become a reputable cyber security consultant who helps businesses stay safe while building a career you can be genuinely proud of.





























































