AI vs Human Intelligence: Key Differences Explained
Discover the key differences between AI and human intelligence, and see how understanding them can give you an edge in work, creativity, and decision-making.

In recent years, AI tools have become increasingly widespread. In 2025, over 378 million people were using AI products globally, with an additional 64 million users joining since 2024 as businesses and individuals increasingly rely on machines. AI adoption highlights the growing popularity of artificial intelligence each year.
AI can now perform many tasks faster than humans in certain fields. For example, AI models have shown their capabilities in reasoning and pattern recognition by scoring up to 9% higher than the average human on complex math tests and comparable results in reading and visual skills.
Machines are data-driven, while human intelligence is shaped by experience, emotions, and learning. In the argument over artificial intelligence vs. human intelligence, people must direct, validate, and enhance outcomes to maintain the distinctively human capacity for comprehension, empathy, and judgment.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The area of computer science known as artificial intelligence (AI) enables machines to think, learn, and make judgments similarly to those of humans. AI can carry out activities automatically, assist in problem-solving, and get better over time by analyzing data. It is transforming our lives, careers, and interactions with technology.
-
AI can recognize speech and images.
-
It helps recommend products or movies.
-
AI can drive cars and operate machines.
-
It learns from experience to make better decisions.
What is Human Intelligence?
Human intelligence is the capacity for thought, learning, and comprehension of the outside environment. It enables us to make choices, solve issues, and adjust to changing circumstances. Each person thinks differently because human intellect is influenced by emotions, creativity, and experiences, unlike that of computers.
-
Humans can imagine and create new ideas.
-
We learn from experiences and mistakes.
-
Emotions and feelings guide our decisions.
-
Humans adapt quickly to new situations.
AI vs Human Intelligence: Key Differences Explained
Artificial intelligence (AI) and human intelligence (HI) have different methods for learning and decision-making. While artificial intelligence (AI) generates answers by identifying patterns, it is unable to fully imitate human creativity, imagination, or emotional awareness.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between AI and human intelligence:
1. Purpose
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): To build machines that are capable of making decisions and solving problems—tasks that have historically required human intelligence.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): To use a variety of cognitive processes, including logic, experience, and intuition, to adjust to novel circumstances.
2. Functionality
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Provides efficiency and consistency by using algorithms, statistics, and patterns to assess information and carry out tasks without being influenced by emotions.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Uses emotions, memories, and thought processes to analyze possibilities, interpret circumstances, and make context-sensitive decisions.
3. Main Components
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Incorporates computer vision, NLP, machine learning, and deep learning to process data and find patterns for tasks.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Combines social skills, emotional intelligence, creativity, perception, and logic to react well in challenging circumstances.
4. Decision Making
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Avoids emotion and emotional impact while solving problems by making data-driven, objective decisions that guarantee predictable and consistent results.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Values, environment, intuition, and emotions all play a role in decision-making, enabling complex and adaptable strategies.
5. Learning Type
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Requires numerous instances and huge datasets to learn. Enhancing training effectiveness for real-world applications requires an understanding of the significance of artificial intelligence.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Swiftly picks up knowledge from one or a few experiences and applies it to novel contexts without repeating.
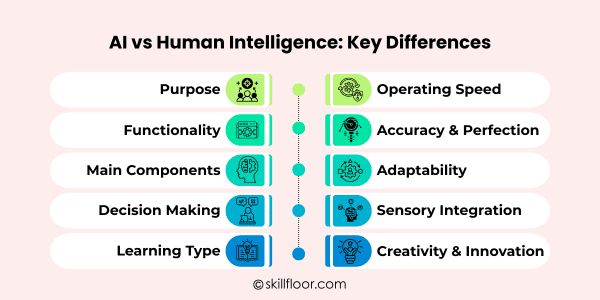
6. Operating Speed
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Handles large amounts of data quickly, offering prompt answers that promote productivity in technological and business operations.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Although humans process information more slowly, they still use context, intuition, and ethical judgment when making decisions.
7. Accuracy & Perfection
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Produces accurate, consistent outcomes when trained appropriately, reducing human error and executing crucial or repetitive activities with great efficiency and dependability.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Fatigue, emotional bias, or inadequate knowledge can all lead to human error, which can impair decision-making accuracy.
8. Adaptability
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Requires reprogramming, retraining, or updating to deal with new situations or unforeseen process changes, which restricts instant flexibility in dynamic circumstances.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Humans are inherently adaptable; they learn from mistakes and modify their tactics without outside help, managing erratic situations with ease and intuition.
9. Sensory Integration
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Compared to human perception abilities, it is limited in its ability to fully comprehend complex environments since it struggles to combine several senses at once.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Humans use a comprehensive integration of sight, sound, touch, and other senses to comprehend their environment, make decisions, and adapt to changes.
10. Creativity & Innovation
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Produces results based on patterns found in the data, but is unable to independently generate novel concepts or ideas.
-
Human Intelligence (HI): Humans are creative beings who can imagine, invent, and express original artistic or problem-solving solutions.
Key Limitations of AI vs Human Intelligence
In addition to being hampered by exhaustion or diminished inventiveness, human intellect is frequently impacted by emotions and biases. Artificial intelligence vs. human intelligence shows that, despite its efficiency and accuracy, AI suffers with emotions, relies on massive datasets, and lacks self-awareness.
The most frequent problems that AI and human intelligence encounter are listed below.
Limitations of Artificial Intelligence
1. No True Emotional Understanding: AI is not able to truly experience, feel, or comprehend human emotions in any meaningful way, but it can imitate emotions and react courteously.
Example: Even though a chatbot might say, "We're sorry for the inconvenience," it is unable to fully understand or sympathize with the customer's emotional state or frustration.
2. Data Dependence: AI cannot readily generate predictions or learn efficiently from sparse bits of data; instead, it depends on massive datasets to function reliably.
Example: If a facial recognition system isn't trained on a variety of faces, it might not be able to recognize someone at first glance, but humans can.
3. Lack of Self-Awareness: AI is incapable of reflecting on choices, thinking critically about its acts, or comprehending the significance of its actions.
Example: Although a recommendation engine can make product recommendations based on a user's browsing history, it is unable to understand the significance of these recommendations or how they meet the demands of the user.
Limitations of Human Intelligence
1. Subjective Decisions: Human decisions are frequently impacted by biases, emotions, and personal preferences, which can result in contradictory assessments and choices in both personal and professional contexts.
Example: A manager may choose to promote a friend or relative over the best applicant, allowing sentimental considerations to take precedence over impartial performance reviews.
2. Fatigue and Lack of Focus: Humans need to sleep, and extended fatigue can impair focus, accuracy, and the likelihood of making mistakes when performing critical jobs.
Example: Following a lengthy hospital stay, a physician may fail to notice important symptoms, which could result in a mistake or poor medical judgment.
3. Limited Creativity: Habits, prior experiences, or entrenched thought patterns might limit human imagination, making it more difficult to come up with completely original concepts or methods.
Example: While AI may generate innumerable new variations based on preexisting patterns, an artist may find it difficult to develop outside of their typical style.
Although human intelligence and AI each have limitations, they can complement one another effectively. Let’s examine how AI can collaborate with human intelligence to achieve better outcomes.
How AI Works Alongside Human Intelligence
AI and human intelligence should be viewed as complementary forces rather than competitors. The debate surrounding artificial intelligence vs human intelligence highlights that humans excel in creativity, intuition, and moral judgment, while AI outperforms in speed, precision, and data processing. When combined, these strengths create new opportunities for development and innovation.
1. Smart Problem-Solving with AI Support
AI effectively provides data-driven insights, while humans use creativity, intuition, and emotional intelligence to make superior decisions in complicated, uncertain situations.
Example: AI in marketing can recommend customer segmentation, but human marketers develop strategies that appeal to consumers' needs and feelings.
2. Seamless Human-AI Collaboration
Easy-to-use AI tools facilitate seamless human-technology connection, guaranteeing productive and successful work.
Example: Teams can concentrate on returns, refunds, or customized product recommendations while AI chatbots handle ordinary customer inquiries.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making Through Augmentation
By supplying pertinent data, AI improves human decision-making, enabling quicker, more accurate, and well-informed decisions while successfully assisting with important business initiatives.
Example: In the retail industry, artificial intelligence suggests inventory changes, but humans make the ultimate decisions based on insights into consumer demand and market conditions.
4. Driving Innovation and Creativity
AI can manage jobs involving a lot of data, allowing humans to concentrate on innovation and creative thinking. Together, they come up with concepts, work through issues, and create original solutions.
Example: When it comes to product development, AI studies trends, but humans create novel features or customer-friendly marketing tactics.
Could AI Replace Human Intelligence One Day?
Many experts believe that AI may eventually achieve human-level intelligence, though opinions on this matter vary considerably. A large survey of 2,778 AI researchers indicates a 50% probability that machines will be able to perform all tasks as well as humans by 2047. However, by 2027, this likelihood drops to only 10%. This illustrates significant progress, but it also highlights the wide disparity in the timelines and confidence levels among researchers.
Some tech executives express bolder predictions. One forecast suggests that AI could soon surpass human intelligence, potentially exceeding the combined intelligence of all humans by 2030. Nonetheless, many experts argue that AI cannot fully replace human intelligence, as it lacks essential human qualities such as emotion, self-awareness, and a true understanding of context.
Even though advancements are happening quickly, most predictions indicate that people and robots will collaborate rather than AI supplanting us entirely. While AI can automate many tasks, human ethics, creativity, and judgment are still essential. That being said, it is still unclear and up for debate whether AI can completely replace human intelligence, including our capacity for meaning and purpose.
The Future of AI and Human Intelligence
Cooperation is key to both human and AI intelligence in the future. While machines manage data, people contribute their creativity, discernment, and empathy to jointly solve difficult problems.
-
AI will automate repetitive tasks.
-
Humans will focus on creative problem-solving.
-
Emotional intelligence will remain uniquely human.
-
AI can analyze vast data quickly.
-
Collaboration boosts efficiency and innovation.
-
Ethical decision-making will rely on humans.
FAQs: AI vs Human Intelligence
Q1: Can AI think like humans?
A: No. AI cannot think like humans. It can analyze data and recognize patterns, but it lacks emotions, self-awareness, and true creativity.
Q2: How does AI help in everyday life?
A: AI helps in daily life by recommending products, managing schedules, driving smart cars, powering virtual assistants, and automating repetitive tasks efficiently.
Q3: Is AI always accurate?
A: AI is not always accurate. Its performance depends on the quality of data. Incomplete or biased data can lead to mistakes.
Q4: Can humans and AI work together?
A: Yes. Humans and AI work best together. Humans add creativity, intuition, and judgment, while AI handles data and repetitive tasks for smarter decisions.
Q5: Will AI replace human jobs completely?
A: AI will not replace humans entirely. While it automates tasks, human creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving remain essential. Collaboration is the future.
Understanding the differences between artificial intelligence and human intelligence shows how each has advantages over the other. Humans contribute creativity, intuition, and empathy to every choice, while AI manages speed, data, and accuracy. The debate between AI vs human intelligence is about collaboration rather than rivalry. We can solve complicated problems, develop more quickly, and make wiser decisions in both our personal and professional lives by fusing human judgment with artificial intelligence's analytical capabilities. By embracing both, we may benefit from technology while preserving our distinctively human characteristics. Togetherness is the way of the future.