Data Science vs Artificial Intelligence: Guiding The Basis
Explore the real deep new differences between Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, their roles, career paths, and how they shape business decisions today.

Artificial intelligence (AI) is a part of everyday life. ChatGPT, Netflix recommendations, Google searches, and even the cameras on our phones display it. Many apps are able to identify faces, comprehend our voices, and recommend things to watch or purchase. AI no longer seems like something from the future as a result.
In the computer industry, data science has emerged as one of the most sought-after competencies. However, this is where the confusion begins. A lot of people confuse artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science. Because they employ these terms in similar ways, it can be challenging for novices to grasp their true meanings.
Some say:
-
“I want to learn AI” — but actually means Data Science.
-
“Netflix uses AI” — but much of it is powered by Data Science.
-
“Data Science is part of AI” — or is it the other way around?
People frequently make poor business decisions that waste time, money, and effort as a result of this misconception, which also causes them to set unreasonable expectations and choose the incorrect professional path.
The World Is Drowning in Data—and Desperate for Intelligence
-
Every day, over 328 million terabytes of data are created, turning the world into a nonstop data-generating machine.
-
Every click, scroll, purchase, and pause is silently tracked, stored, and analyzed.
-
Companies are no longer struggling with lack of data — they’re struggling with lack of clarity and direction.
-
Raw data alone is noise unless someone can turn it into meaning.
-
This is where Data Science steps in to make sense of the chaos.
-
And where Artificial Intelligence steps in to act on that understanding — at speed and at scale.
These two domains are subtly controlling the modern world, from chatbots to self-driving features, from Netflix suggestions to fraud detection.
What is Data Science?
Understanding—converting disorganized, overwhelming data into insights, patterns, forecasts, and narratives that people and organizations can act upon—is the goal of data science.
A Data Scientist is part detective, part analyst, part storyteller, asking questions like:
-
Why are customers leaving?
-
What factors drive sales?
-
What will happen if we change this strategy?
-
Where are we wasting money?
The goal is not only to gather data but also to derive significant insights that direct more intelligent choices and tactics.
Key Steps in Data Science
-
Collect data
-
Clean and prepare data
-
Explore and analyze data
-
Build predictive or descriptive models
-
Visualize and communicate results
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence focuses on behavior, developing systems that are capable of learning, reasoning, perceiving, making decisions, and acting on their own without constant human oversight or direction.
It powers technologies like:
-
Chatbots and virtual assistants
-
Recommendation engines
-
Face and voice recognition systems
-
Autonomous vehicle features
-
Smart fraud detection
AI's main goal is not only to comprehend the environment but also to accomplish artificial intelligence objectives, operate in it, and automate large-scale decisions and actions.
Key Subfields of AI
-
Machine Learning
-
Deep Learning
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
-
Computer Vision
-
Reinforcement Learning
The Core Purpose: What Problem Each One Solves
Purpose of Data Science
Data Science is mainly about:
1. Finding Hidden Patterns
Large datasets include patterns that are invisible to the human eye, but data science finds them.
2. Discovering Important Trends
It examines past data to identify patterns that might effectively direct corporate initiatives.
3. Explaining Business Performance
Data science offers lucid insights for decision-making by helping to explain why specific business outcomes take place.
4. Predicting Future Outcomes
It helps businesses make confident plans by using historical data to predict future outcomes.
5. Supporting Decision Making
Managers and teams may make more informed, fact-based business decisions with the help of data-driven insights.
6. Optimizing Processes Efficiently
It assists in locating inefficiencies and making recommendations for enhancements to boost performance and operational efficiency.
Data science is analysis-driven and insight-driven, assisting businesses in identifying patterns, trends, and practical insights from data to enhance strategy planning and decision-making.
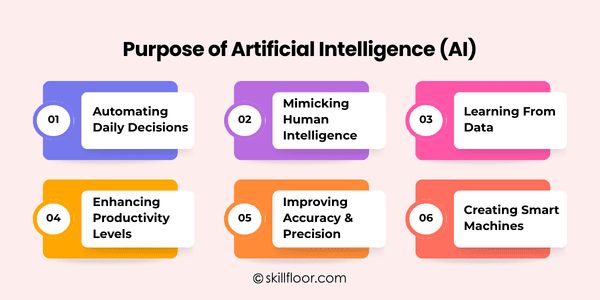
Purpose of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is mainly about:
1. Automating Daily Decisions
Artificial intelligence (AI) speeds up routine decision-making for machines, saving human labor and improving task efficiency.
2. Mimicking Human Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are capable of comprehending, learning, and solving issues in a manner akin to that of humans.
3. Learning From Data
Large data sets can be analyzed by AI to automatically increase performance and accuracy over time.
4. Enhancing Productivity Levels
AI boosts productivity by automating jobs, freeing up humans to concentrate on more difficult tasks.
5. Improving Accuracy & Precision
AI systems lower human error in operations, forecasting, and decision-making in a variety of industries.
6. Creating Smart Machines
AI makes it possible for robots to act sensibly, adapt, and carry out activities that typically call for human judgment.
AI allows robots to act intelligently since it is behavior-driven and automation-driven. Learning, reasoning, and problem-solving are examples of AI components that enable systems to successfully imitate human behavior.
Data Science vs. Artificial Intelligence: A Side-by-Side Comparison
1. Goal
Data Science: The goal of data science is to produce lucid insights, recognize trends, and offer valuable direction for making decisions.
AI: The main goals of AI are process automation, intelligent decision-making, and self-governing behavior.
2. Focus
Data Science: Asking questions, evaluating data, and effectively communicating insights to help decisions are the main goals of data science.
AI: AI focuses on creating systems, models, actions, and optimization, effectively encompassing several AI domains.
3. Output
Data Science: Data science helps people make better decisions by providing forecasts, reports, dashboards, and actionable insights.
AI: AI creates intelligent features, functional goods, and automated systems that run without continuous human supervision.
4. Human Involvement
Data Science: By directing actions based on analysis and interpreted findings, data science keeps people informed.
AI: AI systems frequently operate autonomously, making choices and carrying out tasks without human oversight or interference.
5. Skillsets
Data Science: To effectively extract relevant insights, data science includes statistical analysis, visualization, problem-solving, and domain expertise.
AI: Programming, machine learning, algorithm design, and model optimization are necessary for AI to effectively build intelligent, autonomous systems.
6. Business Usage
Data Science: Businesses may act strategically and confidently by using data science to support choices, find opportunities, and explain patterns.
AI: AI promotes efficiency and creativity by automating procedures, scaling activities, and creating intelligent solutions that run on their own.
How They Work in Practice: Workflow Comparison
Data Science Workflow
-
Collect Data
-
Clean and Preprocess Data
-
Analyze Data
-
Visualize Data
-
Find Insights
-
Help Business Make Decisions
Output: Reports, dashboards, insights, predictions
AI Workflow
-
Collect Data
-
Train Model
-
Test Model
-
Optimize Model
-
Deploy Model
-
System Makes Automatic Decisions
Output: Intelligent system, automation, predictions, actions
Tools & Technologies Used
Data Science Tools
-
Python, R, SQL
-
Pandas, NumPy
-
Excel, Power BI, Tableau
-
Statistics and Probability
AI Tools
-
Python
-
TensorFlow, PyTorch
-
Neural Networks
-
NLP, Computer Vision
-
Deep Learning frameworks
Real-World Examples
Data Science Examples
-
Sales performance dashboard
-
Customer segmentation analysis
-
Stock price trend analysis
-
Marketing campaign effectiveness analysis
-
Business forecasting models
AI Examples
-
Chatbots like ChatGPT
-
Face recognition systems
-
Voice assistants (Siri, Alexa)
-
Self-driving cars
-
Fraud detection systems
Where Both Work Together
-
Netflix recommendations
-
Amazon product suggestions
-
YouTube video recommendations
-
Spotify playlists
Data science helps businesses better understand their customers and make evidence-based decisions by analyzing patterns, trends, and preferences from data.
AI uses data insights to make content recommendations automatically. By learning user preferences and habits, AI personalizes user experiences and improves interactions without the need for human intervention.
Career Perspective: Data Scientist vs AI Engineer
Data Scientist
-
Works more with data, analysis, insights
-
Focuses on business problems
-
Uses statistics, SQL, Python, dashboards
-
Cleans and preprocesses raw data for accurate results
-
Builds predictive models to forecast future trends
-
Communicates findings through reports and visualizations
Goal: By analyzing data, identifying trends, forecasting results, and offering practical insights that direct tactics and enhance overall corporate performance, data scientists assist organizations in making better decisions.
AI Engineer
-
Works more with models and systems
-
Focuses on automation and intelligence
-
Uses deep learning, neural networks, deployment
-
Trains AI models using large datasets for learning and improvement
-
Evaluates model performance to ensure accuracy and reliability
-
Deploys and integrates AI systems into real-world applications
Goal: By creating, training, and implementing models that automate choices, learn from data, and provide clever, effective answers in practical applications, AI engineers create intelligent systems.
When Should a Company Use Which?
Use Data Science When:
-
You want insights and reports
-
You want to understand customers
-
You want better business decisions
-
You want predictions, not automation
-
You want to identify trends and patterns in data
-
You want to optimize business processes based on analysis
Use AI When:
-
You want automation
-
You want machines to make decisions
-
You want smart products
-
You want scalable intelligent systems
-
You want to improve efficiency with minimal human effort
-
You want real-time data-driven insights and actions
Use Both When:
-
You want intelligent, data-driven products
-
You want automated systems informed by deep insights
-
You want personalized customer experiences at scale
-
You want predictions and actions working together seamlessly
-
You want to optimize business decisions using smart automation
-
You want to combine analytics and AI for maximum impact
Common Myths & Misconceptions
1. Data Science = AI
Many people think that AI and data science are synonymous, but AI is more concerned with intelligent systems, whereas data science is more concerned with insights.
2. Must Know Deep Learning
To become a data scientist, you don't always need to understand deep learning; statistics, analysis, and fundamental machine learning are often enough.
3. AI Always Needs Huge Data
AI can efficiently use transfer learning, synthetic data, or pre-trained models with small or intermediate datasets.
4. AI Will Replace Data Scientists
While AI helps data scientists, it cannot completely take the role of human judgment, creativity, and subject-matter expertise in decision-making.
5. Data Science Is Only Coding
Data science requires more than simply programming and coding abilities; it also requires problem-solving, analysis, visualization, and business expertise.
6. AI Is Only for Tech Experts
With low-code and no-code platforms, AI is becoming more widely available, making it usable for non-technical professionals and commercial users.
Future Trends in Data Science and Artificial Intelligence
1. AI-Powered Analytics
AI-powered analytics helps businesses make correct, real-time choices without human intervention by combining machine learning and data analysis to provide quicker, more intelligent insights.
2. AutoML
Even non-experts may rapidly and effectively design correct machine learning models thanks to Automated Machine Learning (AutoML), which shortens development times.
3. Generative AI + Data Science
When generative AI and data science are combined, synthetic data, predictive models, and innovative solutions can be created, improving decision-making and innovation in a variety of industries.
4. Edge AI
Faster processing, real-time insights, and smarter apps directly on smartphones, IoT devices, and sensors are made possible by AI operating on devices rather than the cloud.
5. Explainable AI (XAI)
Explainable AI ensures responsibility and confidence by assisting enterprises in comprehending how AI models make decisions. Automation testing can be incorporated into AI workflows with its help.
6. Decision Intelligence
AI, analytics, and human expertise are all combined in decision intelligence to enhance complex decision-making, resulting in more intelligent plans, more accurate forecasts, and successful commercial outcomes.
As we've seen, understanding how data science and artificial intelligence interact is more important than picking one over the other. By identifying patterns and insights we may otherwise overlook, data science assists us in making sense of the never-ending streams of data. AI transforms such knowledge into action, enabling intelligent systems to function quickly and extensively. Businesses and professionals may make more informed decisions, develop individualized experiences, and produce really innovative goods when they combine the two. In today's fast-paced world, understanding the differences and how each enhances the other is crucial. The more you understand the differences between artificial intelligence and data science, the more prepared you will be to move forward with confidence and make the most of these capabilities.































































