The Foundation of Artificial Intelligence
The foundation of AI, including its core principles, applications in various industries, and its growing impact on our world, from healthcare to finance.

When I first started studying the Foundation of Artificial Intelligence, I was taken in by the potential and promise that AI offered for a range of industries, including healthcare and finance. I recall being both excited and scared by the complex nature of the area when I enrolled in my first artificial intelligence course. However, as I learned more, I came to understand that the fundamentals of AI are ones that everybody with a logical mind and a passion for learning can understand. It combines computer science, mathematics, and philosophy; it's not just about data and algorithms. The journey showed me that the foundation of artificial intelligence (AI) is based on core concepts that have developed over many years, enabling machines to reason, learn, and adapt. In this blog, I want to discuss how these ideas serve as the foundation for artificial intelligence today as well as its increasing significance in several fields.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
A field of technology known as artificial intelligence, or simply AI, allows machines to imitate human qualities such as learning, problem-solving, and adapting to situations. Computers can process information in ways that are comparable to human mental procedures, including pattern recognition, decision-making, and result estimation, due to the foundation of artificial intelligence. AI can be described as a computer brain that can understand complex information and learn from data.
Though artificial intelligence (AI) may seem like an advanced idea, its roots can be traced back to the 1950s, when early computer scientists started thinking about how machines could imitate some characteristics of human intelligence. The basis of artificial intelligence has expanded over time to include methods from a variety of disciplines, such as data processing, cognitive science, and mathematics. With this evolution, AI development companies play a key role in applying these techniques to real-world systems. AI can perform a broad range of jobs and applications across sectors due to this combination.
The Foundation of AI: Core Principles and Components
Artificial intelligence's basis is based on some fundamental ideas and elements that enable it to function in a variety of situations. Let's explore the fundamental elements that form this foundation:
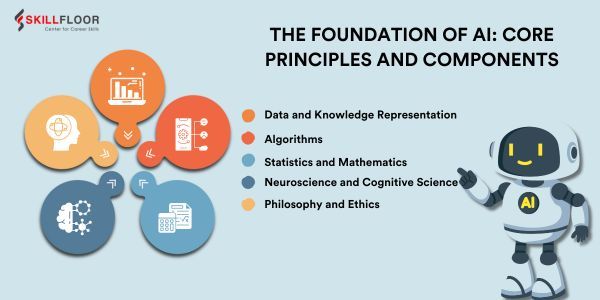
1. Data and Knowledge Representation
The foundation of artificial intelligence is data. An AI system needs huge amounts of data to find patterns and acquire insights to "learn" and make decisions. The goal of knowledge representation, on the other hand, is to organize this material such that computers can understand, store, and retrieve it. The core of artificial intelligence is knowledge and data, which work together to allow it to understand unprocessed data.
2. Algorithms
An AI system can assess data and draw conclusions from it because of algorithms, which are detailed instructions or sets of rules. These algorithms have become more and more advanced, enabling AI to perform incredibly difficult jobs like language translation and image identification. These algorithms provide the basis of artificial intelligence, allowing it to learn from data and make predictions.
3. Statistics and Mathematics
The foundation for understanding and evaluating data patterns is mathematics, especially statistics and calculus. Statistical techniques help in the development of models that show connections in data, enabling AI to make sensible choices. AI would have very little predictive capacity without mathematics.
4. Neuroscience and Cognitive Science
Researchers have learned how to reproduce specific cognitive processes in AI systems by examining the human brain. By providing a blueprint of human learning, memory, and decision-making, cognitive science and neuroscience help build more "human-like" robots, which form the basis of artificial intelligence.
5. Philosophy and Ethics
In AI, ethical issues are becoming more and more important. By establishing guidelines for how AI should function and be used in society, concerns about privacy, biases, and responsibility help to build the field's foundation. Ethical standards ensure that advancements in AI protect individual rights and are consistent with the values of society.
Together, these fundamental components form a strong framework that supports artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence systems wouldn't be able to carry out significant, practical tasks without this foundation.
Importance of Artificial Intelligence
It is impossible to understate the importance of artificial intelligence in the modern world. AI is becoming an essential part of many fields, not only a tool for scientists or companies in IT. AI can analyze data more quickly than a human may due to its foundation, which offers priceless insights in industries like healthcare, banking, retail, and education.
For example, in healthcare, AI-driven technologies may evaluate medical images, predict the course of diseases, and even provide individualized therapies in the healthcare industry. AI improves service quality and security in the financial industry by helping with fraud detection and individualized financial advice. The fact that artificial intelligence is being used in many fields shows its increasing significance and demonstrates how a strong basis in AI can result in revolutionary advances across a range of industries.
Key Areas of Application in Artificial Intelligence
In recent years, the significance of artificial intelligence has grown significantly. AI was once a specialist technology used only in tech companies and research labs, but it is now a part of our daily lives. The basis of artificial intelligence enables AI systems to operate in a variety of settings and fields, changing our methods of problem-solving, collaboration, and work.
1. Healthcare
AI is transforming patient care in the healthcare industry. By analyzing medical data, machine learning algorithms help physicians in diagnosing patients more quickly and accurately. An AI system, for example, may analyze thousands of radiology images to find patterns that point to illnesses, helping doctors spot abnormalities early. These computers can handle huge amounts of data far more quickly than people, potentially saving lives, thanks to the basis of artificial intelligence.
2. Finance
AI is used by financial organizations to monitor risks, identify fraudulent activity, and customize client experiences. Real-time transaction data is analyzed by AI algorithms, which highlight any patterns that might point to fraud. These systems can adjust and learn from fresh data due to the foundation of artificial intelligence, which gradually increases their effectiveness.
3. E-commerce and retail
Retailers may better understand customer preferences and adjust their marketing strategies with the help of AI. The development of artificial intelligence directly resulted in the creation of recommendation engines, which provide product recommendations based on browsing or previous purchases. Retailers may also minimize waste and optimize stock levels with the aid of AI-powered inventory management solutions.
4. Manufacturing and Logistics
Predictive maintenance programs and AI-driven robots have simplified operations in the manufacturing sector, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency. By predicting problems with machinery before they occur, the basis of artificial intelligence promotes innovations that help businesses avoid expensive delays.
5. Education
Through the personalization of learning experiences, AI is revolutionizing the education industry. Adaptive learning systems make education more accessible and customized by adjusting to each student's unique pace and learning preferences. The development of systems that can meet a range of learning requirements and maximize academic results is made possible by the foundation of artificial intelligence in this case as well.
The Role of AI Courses in Building a Strong Foundation
Enrolling in an AI course can be quite helpful for anyone who wants to learn about and work with artificial intelligence. The fundamental topics of artificial intelligence, such as data analysis, machine learning, and algorithm design, are covered in AI courses.
In addition to learning about the mathematical foundations of AI, finishing an AI course gives you hands-on experience using tools and techniques that aid in the development of intelligent systems. You can use AI in a variety of real-world situations due to this strong foundation of theory and practice.
Ethics and the Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence
An important factor in the development of AI is ethics. The need to make sure that AI systems are managed properly is growing as they keep entering more aspects of daily life. Artificial intelligence is built on ethical principles to produce systems that preserve flexibility, prevent bias, and protect privacy.
Biased AI systems, for example, can produce unfair results in industries like banking and recruiting, which can have a big impact on people's lives. Developers ensure that AI functions for everyone by integrating ethical issues into the basis, producing impartial and equitable results.
Challenges in Building the Foundation of AI
Developing a strong artificial intelligence foundation presents a unique set of difficulties.
- Data Quality
The quality of the data is essential for AI systems. Biased or inaccurate data can result in AI models that are defective and may yield unfair results or inaccurate projections. Building a strong foundation for AI requires ensuring data quality.
-
Complexity of Algorithms
Algorithms must advance in complexity as AI systems take on more challenging jobs. These algorithms can be difficult to design, test, and carry out; they require a complete understanding of the data and the problem.
-
Ethical Concerns
As previously said, ethics is essential for the development of artificial intelligence. It can be challenging to strike a balance between ethical issues and technological innovation, particularly as AI becomes more powerful.
-
Interpretability
A lot of AI models, particularly deep learning algorithms, function as "black boxes," making it challenging to understand how they reach particular judgments. Since interpretability is essential to building trust in AI, this lack of transparency is an important issue.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The foundations of artificial intelligence will keep developing, influencing how society and technology develop in the future. AI's impact will grow as new application areas appear as it advances in intelligence.
-
Enhanced Human-AI Collaboration
Future AI systems are likely to collaborate more closely with people, helping with activities that call for both AI efficiency and human judgment. For these systems to smoothly integrate with human operations, the Artificial Intelligence basis will be essential.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Advances
The field of artificial intelligence called natural language processing (NLP) is devoted to understanding and creating human language. We are confident that as NLP develops, AI systems will interact with humans in a more organic and meaningful way, increasing their value in personal help, education, and customer service.
-
AI in Climate and Sustainability Solutions
The ability of AI to handle data may help address global issues like climate change. AI may be used to predict changes in the environment, optimize energy use, and create resource management systems that are more effective. The development of these significant solutions will be helped by the foundation of artificial intelligence.
-
Improving Inclusion and Accessibility
AI can help people with problems by developing technologies that facilitate learning, movement, and communication. For example, those who might not be able to read or write can access information due to speech recognition and translation tools.
Overall, a combination of data science, algorithms, cognitive science, and ethical issues forms the basis of artificial intelligence. Together, these components make a powerful tool that can imitate human intelligence and revolutionize entire sectors. Beyond technology, this foundation is significant because it offers solutions that enhance productivity, judgment, and quality of life.
Understanding the fundamentals of artificial intelligence is essential for everybody working with AI in their daily life, not just those developing AI systems. This fundamental understanding helps in our understanding of artificial intelligence's operation, possible advantages, and associated responsibilities. The basis of AI will direct its uses as it develops further, ensuring that it continues to be a force for positive change.