Benefits of Business Analytics
Don’t miss out on growth! Explore how business analytics predicts outcomes, improves decision-making and mitigates risks to transform your business.

Nowadays, businesses are constantly looking for ways to get better and stay ahead of competitors. One powerful tool they use to do this is business analytics. If you're not familiar with the term, don’t worry! Let me explain what business analytics is, how it works, and why it’s so important.
What is Business Analytics?
Simply put, business analytics is the process of using data to make better decisions. It involves collecting and analyzing data to understand trends, find problems, and make smart choices. For example, if you're running a business and want to know which products sell the best, you can use business analytics to look at past sales data and find out.
Analytics uses tools and techniques, such as data analysis, statistical methods, and sometimes advanced technology like artificial intelligence (AI), to help businesses figure out what works and what doesn't.
Different Types of Business Analytics
There are a few different types of business analytics, and each one helps businesses in different ways. Here’s a breakdown:
-
Descriptive Analytics: This type of analytics helps businesses understand what has happened in the past. For example, it can show how many products were sold last year or how many customers visited a store.
-
Diagnostic Analytics: This goes a step further by explaining why something happened. For instance, if sales went down last month, diagnostic analytics could help figure out if it was because of poor marketing, competition, or something else.
-
Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics looks at past data to forecast what might happen in the future. For example, if sales tend to increase during the holidays, this type of analysis can help predict how much you’ll sell next season.
-
Prescriptive Analytics: This is the “what should we do next” type of analysis. It doesn’t just predict the future but suggests actions to take. For example, if you predict lower sales, prescriptive analytics might suggest offering discounts or running a special promotion.
-
Cognitive Analytics: This is the most advanced form and uses AI to make decisions. It mimics human thinking to solve complex problems, like detecting fraud or personalizing customer experiences.
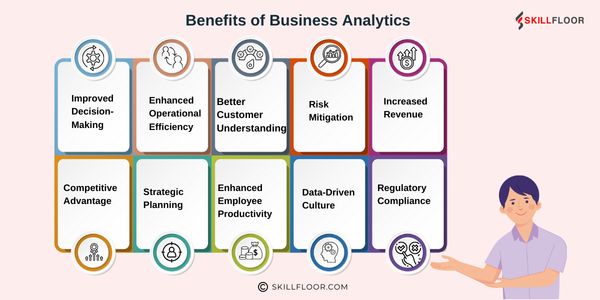
Benefits of Business Analytics
Now that we know what business analytics is and the different types, let’s look at the key benefits it brings to businesses.
1. Improved Decision-Making
Business analytics provides insights from data, enabling leaders to make decisions based on evidence rather than intuition. By analyzing historical data, organizations can:
-
Spot trends: Identify recurring patterns in sales, customer behavior, or operational performance.
-
Predict outcomes: Use predictive analytics to estimate the impact of potential business moves, such as launching a new product or entering a new market.
-
Optimize decisions: Tools like dashboards and real-time analytics allow businesses to adjust strategies quickly in response to changes in the market or performance metrics.
For example, data analytics in e-commerce businesses might use analytics to decide which product categories to promote during a specific season based on past purchasing trends.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Inefficiencies in processes cost businesses time and money. Analytics tools help identify these inefficiencies by:
-
Analyzing workflows: Detecting bottlenecks in production or service delivery processes.
-
Resource optimization: For instance, predictive analytics can forecast demand, ensuring that businesses maintain the right level of inventory—reducing overstock and stockouts.
-
Process automation: Business analytics integrates with automation tools, enabling repetitive tasks to be handled by software while humans focus on strategic tasks.
A logistics company, for instance, could use analytics to optimize delivery routes, saving fuel costs and improving delivery times.
3. Better Customer Understanding
Understanding customer preferences and behavior is crucial for tailoring products, services, and marketing. Analytics enables businesses to:
-
Segment customers: By grouping customers based on demographics, purchasing behavior, or interaction patterns, businesses can create targeted campaigns.
-
Improve customer experience: Insights help refine user interfaces, enhance customer support, and create personalized offers.
-
Track customer journey: Analytics reveals touchpoints where customers engage with the brand, helping businesses optimize their marketing funnel.
For example, streaming platforms like Netflix use analytics to recommend shows based on a user’s viewing history, boosting engagement and retention.
4. Risk Mitigation
Every business faces risks, from market volatility to cybersecurity threats. Business analytics helps minimize these risks through:
-
Predictive modeling: Anticipate potential issues like equipment failures, financial shortfalls, or project delays before they occur.
-
Fraud detection: Analytics systems flag suspicious transactions or activities in real time.
-
Scenario analysis: Businesses can simulate different market conditions to assess potential risks and plan mitigating actions.
For example, a bank might use analytics to detect unusual patterns in transactions, helping prevent fraud.
5. Increased Revenue
By identifying opportunities for growth and optimization, business analytics helps improve profitability:
-
Revenue generation: Analytics identifies high-performing products, services, or customer segments to prioritize investment.
-
Price optimization: Tools analyze market trends and customer demand to suggest the best pricing strategies.
-
Sales funnel analysis: Businesses can pinpoint where customers drop off during their journey and address those gaps to improve conversion rates.
An example is retail chains using sales data to create promotional offers that increase both foot traffic and average purchase value.
6. Competitive Advantage
In today’s competitive environment, businesses that utilize data-driven insights can outpace their competitors. Business analytics provides:
-
Market intelligence: A clear understanding of market trends and customer preferences gives businesses an edge.
-
Benchmarking: Analytics allows organizations to compare their performance against industry standards or competitors, identifying areas for improvement.
-
Innovation enablement: By predicting future customer needs, businesses can innovate ahead of competitors.
For instance, Amazon leverages analytics to optimize its supply chain and recommend products, staying ahead of other retailers.
7. Strategic Planning
Long-term success depends on effective planning, and analytics plays a critical role by:
-
Forecasting: Predicting market trends and financial outcomes based on past and present data.
-
Measuring success: Analytics helps track key performance indicators (KPIs) like revenue growth, cost savings, or customer satisfaction, enabling businesses to stay on course.
-
Scenario planning: Businesses can test different strategies in a simulated environment to understand potential outcomes.
For example, airlines use demand forecasting to adjust flight schedules, pricing, and resource allocation.
8. Enhanced Employee Productivity
Employees are a company’s most valuable resource, and analytics can boost their productivity by:
-
Identifying performance trends: Managers can track metrics like task completion rates or sales performance to address inefficiencies.
-
Optimizing schedules: Analytics tools can create optimal work schedules, reducing downtime and burnout.
-
Focusing efforts: Automation of repetitive tasks, such as data entry or basic customer queries, frees employees to focus on higher-value activities.
For instance, HR analytics can identify employee training needs and improve their skills and productivity.
9. Data-Driven Culture
When data is embedded in an organization’s decision-making process, it creates a culture of accountability and innovation:
-
Shared insights: Analytics tools make data accessible across departments, encouraging collaboration.
-
Continuous improvement: Regular performance tracking encourages teams to refine their strategies and achieve goals.
-
Empowerment: Employees are empowered to make decisions based on data, leading to better outcomes.
An example is a tech company using a central analytics platform where marketing, sales, and product teams share performance data to align their strategies.
10. Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with regulations is critical, especially in industries like finance, healthcare, and technology. Business analytics helps by:
-
Monitoring compliance metrics: Tools can track whether the business is adhering to legal standards, such as data privacy laws.
-
Streamlining audits: Analytics systems maintain a detailed record of transactions, making it easier to meet audit requirements.
-
Identifying risks: Analytics helps identify areas where the organization might inadvertently violate regulations.
For example, a healthcare organization might use analytics to ensure patient data is stored and used in compliance with HIPAA guidelines.
Real-Life Examples of Business Analytics in Action
Let’s take a look at how business analytics works in different industries:
-
Retail: Stores can use business analytics to track sales and figure out which products are most popular. This helps them adjust their inventory and offer better deals to customers.
-
Finance: Banks and financial institutions use analytics to detect fraud by spotting unusual activity in accounts. They can also predict future trends in the market to make smarter investments.
-
Manufacturing: Factories use predictive analytics to schedule maintenance on machines before they break down. This helps them avoid expensive repairs and downtime.
-
Customer Service: By analyzing customer feedback, businesses can see what customers like or don’t like and improve their service. For example, if customers are unhappy with long wait times, they can make changes to improve speed.
Challenges in Using Business Analytics
Although business analytics is incredibly useful, it’s not always easy to use. Here are some common challenges businesses face:
-
Bad Data: If the data is incomplete or incorrect, it can lead to poor decisions. This is why data quality is so important.
-
Cost of Tools: Setting up the right analytics tools can be expensive, and not every business has the budget for it.
-
Lack of Knowledge: It’s one thing to have data; it’s another to know how to analyze it. Many businesses struggle because they don’t have the skills or expertise to use the data properly.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees might be used to making decisions based on experience or gut feeling. It can be tough to get everyone on board with using data to drive decisions.
The Future of Business Analytics
The future of business analytics is exciting. As technology continues to improve, businesses will be able to make even faster and smarter decisions. For example, AI and machine learning will make it easier to analyze data in real-time, giving businesses the ability to adjust strategies on the fly. Automation will also play a big role, making processes more efficient and reducing human errors.
business analytics is a powerful tool that helps companies make smarter decisions, improve efficiency, and stay ahead of their competitors. Whether you’re managing a small business or working for a large corporation, using data to guide your decisions is essential in today’s world.
As we’ve seen, the benefits of business analytics are clear: better decisions, lower costs, happier customers, and improved efficiency. If you’re not already using business analytics in your business, now is the perfect time to start. With the right tools and knowledge, you can unlock the full potential of your business and stay ahead in a competitive market.






























































