Components of Cloud Computing in Simple Terms
The power of cloud computing: secure, scalable, and accessible data storage. Don't miss out on cost-saving, flexible solutions for work and life!

Imagine your everyday routine: utilizing Google Docs to collaborate with colleagues, uploading family photographs to Google Photographs, or watching your favorite TV series on Netflix. Despite their seemingly mundane appearance, cloud computing powers all of these operations. Many of the modern comforts of technology would not be possible without it.
You can access data, programs, and storage online through cloud computing rather than depending on your device. It's like not owning tools but borrowing them instead. This system is powered by trusted behemoths like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft, who provide dependable, safe, and easy-to-use platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure for daily convenience.
When using cloud computing, security is key. Platforms like Dropbox and Google Drive use cutting-edge encryption and international standards to safeguard your data. Your data are safe, whether they are in transit or at rest, due to the components of cloud computing, such as secure storage and frequent upgrades.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is part of our daily lives, whether we realize it or not. The technology behind the programs we enjoy, like Spotify's music streaming and Google Drive's document storage, is what makes them possible. It's similar to having a digital storage vault that you can use from anywhere at any time without worrying about running out of room.
Cloud computing is essentially the ability to access data, apps, or storage via the internet rather than relying on a physical device. If you're keen to learn more, Cloud Computing Courses are a terrific method to grasp how scalable and dependable it is, which will help you realize its full potential.
The Rising Importance of Cloud Computing for Everyone
1. Accessibility Anywhere
Cloud computing makes it easier than ever to work remotely, study online, and remain in touch with loved ones by enabling you to access data and tools from any location.
2. Cost Savings
Cloud computing reduces expenses for both people and enterprises by eliminating the need for real servers and infrastructure, freeing them up to concentrate on other crucial concerns.
3. Scalability
Whether your business is small and just getting started or is expanding, cloud computing adapts to your requirements and offers flexible solutions without requiring you to make an upfront investment in costly infrastructure.
4. Data Security
Cloud services provide safe spaces for storing sensitive data with frequent updates and sophisticated encryption, guaranteeing that your data is safe from online attacks.
5. Collaboration Made Easy
Teams can collaborate easily and in real time, regardless of their location, due to cloud-based technologies like Google Docs.
6. Eco-Friendly Technology
Cloud computing encourages more sustainable, greener technological practices that help you lower your carbon footprint by eliminating the need for energy-intensive physical servers.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Efficiency
Businesses and individuals may save money by only paying for the resources they use thanks to cloud computing, which does away with the need for costly hardware and upkeep.
2. Flexibility and Scalability
Explore the scope of cloud computing in dynamic situations by effortlessly adjusting resources to fit your demands, whether scaling up for company growth or down during slower seasons.
3. Remote Accessibility
Access information, programs, and resources from any location, facilitating easy and comfortable remote work, teamwork, and personal task management.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Teams may collaborate on the same files in real-time using cloud services like Google Workspace, which increases collaboration and productivity even when people are in different places.
5. Automatic Updates
Because cloud services manage software updates automatically in the background, you may take advantage of the newest features and security enhancements without having to manually download anything.
6. Data Backup and Recovery
By ensuring that your data is routinely backed up, cloud computing gives you peace of mind and facilitates recovery in the event of unplanned disasters or inadvertent deletions.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
1. Internet Dependency
An internet connection that is steady is essential for cloud computing. Any disruption may result in hold-ups or hinder access to critical information and programs.
2. Data Security Risks
Even though security is a top priority for cloud providers, keeping private data online can still be dangerous due to data breaches and illegal access, particularly if security procedures aren't followed.
3. Limited Control
Utilizing third-party cloud services entails relying on their infrastructure, which limits your control over features, upgrades, and service management.
4. Hidden Costs
Even while cloud computing is inexpensive, unforeseen costs like data transfer fees or upgrading to higher-tier services can occasionally make it more costly than first thought.
5. Downtime
Outages or technical problems can periodically affect even the best providers, disrupting service access and affecting user and company productivity.
6. Compliance Challenges
Making sure cloud services adhere to compliance standards in sectors with stringent laws can be difficult and may need extra agreements or monitoring.
Essential Components of Cloud Computing
1. Front-End Components
Let’s start with what you see and use every day: the front end.
Consider launching a program or website such as Dropbox, Gmail, or Netflix. That is cloud computing's front end. It's the section you engage with. Similar to a restaurant menu, where you see the food but not the kitchen when you send an email or view a movie online, you are interacting with the front end, one of the components of cloud computing.
Front-end components include:
-
User Interface (UI): What you see on your screen is the user interface, which is intended to make interactions and navigation simple and straightforward.
-
Client Devices: Phones, tablets, and PCs that connect to the cloud are examples of client devices that help you easily access data and services.
Consider it the face of cloud computing; it is the reason it is accessible and user-friendly.
2. Back-End Components
Let's now examine the inner workings of the cloud. Similar to a car's engine or a restaurant's kitchen, the back end is one of the most important components of cloud computing. Everything you use and see on the front end is powered by it.
The back-end components include:
-
Servers: These are strong computers with storage and software capabilities. The photographs you post to Google photographs, for instance, are preserved on a server.
-
Storage: This is the location of all your info. It may be compared to a digital file cabinet that holds your papers, movies, and images.
-
Databases: Databases effectively store and retrieve data. For instance, a database is used by Netflix to store your viewing preferences.
-
Middleware: This serves as a link between the front end and the back end, facilitating seamless communication between both.
The back end makes sure everything functions well behind the scenes for you.
3. The Network
The network serves as the highway that links your back end, which is where the magic happens, and your front end, which is what you utilize. It is an essential component of cloud computing concepts since the cloud would not exist or operate without a network.
The most popular network for cloud computing is the Internet. It enables communication between your computer and the servers that house your data. As the delivery system that transfers data from one location to another without interruption, this network is one of the essential components of cloud computing.
For example:
-
The network sends the YouTube video to your device from a server when you watch it.
-
The network makes sure your updates are stored and updated instantly if you're using Google Docs.
It would be slower and less efficient to use cloud computing without a dependable network.
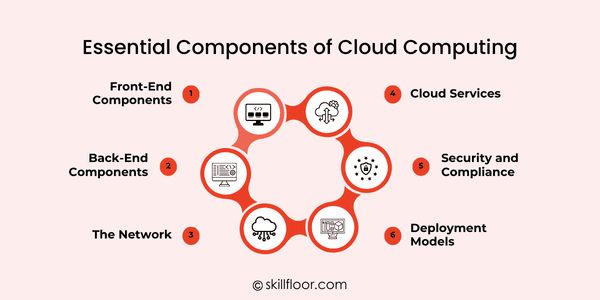
4. Cloud Services
Cloud services are similar to the many tools available for usage or rental in the cloud. Typically, they fall into one of three categories:
-
SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS is the most popular kind of cloud service, allowing you to utilize applications online without having to install any software. Key ideas of cloud computing are demonstrated by examples such as Gmail and Zoom, which smoothly integrate with Big Data.
-
PaaS (Platform as a Service): PaaS provides a platform for app developers to create and test applications. It supports fundamental cloud computing ideas in app development and makes dealing with Big Data easier using tools like Google App Engine.
-
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): IaaS lays the groundwork by leasing storage and virtual machines. Big Data is effectively managed by services like AWS and Azure, which emphasize the core ideas of cloud computing that underpin scalable infrastructure solutions.
5. Security and Compliance
Cloud computing security is a major concern. Your data must be protected, after all!
To keep your information secure, cloud providers use:
-
Firewalls: Firewalls protect your data by preventing unauthorized access and guaranteeing that only reliable sources are allowed access.
-
Encryption: Encryption jumbles your data into a safe format that only those with the right keys or credentials can access.
-
Regular Updates: By fixing vulnerabilities, defending systems against fresh attacks, and safeguarding your data, regular upgrades improve security.
Adhering to rules and regulations is the essence of compliance. Businesses that handle personal data, for example, are required to abide by privacy regulations such as GDPR. It is one of the key components of cloud computing, guaranteeing the safety and security of your data.
Cloud computing isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different deployment models suit different needs:
-
Public Cloud: This is comparable to a shared gym. It is run by a third party and is open to everyone. Google Drive and Dropbox are two examples. Although less private, it is more affordable.
-
Private Cloud: Consider this your own exercise facility. It is dedicated to a single user or entity. Banks and other organizations that handle sensitive data frequently employ private clouds.
-
Hybrid Cloud: You get the best of both worlds here. Both private and public clouds are combined. For instance, a business may utilize a private cloud for sensitive data while storing regular files on a public cloud.

How the Components of Cloud Computing Work Together
1. Front-End Interface
Front-end apps, such as Gmail or Netflix, offer an intuitive user experience that is linked to robust back-end services.
2. Back-End Operations
By supporting crucial components of the Cloud Revolution, the back end manages data processing and storage, guaranteeing smooth operation and user experiences.
3. Networks Connect Everything
Networks serve as the link between the user's front end and back end, allowing for real-time access to cloud services from any location in the globe.
4. Cloud Services Integration
From straightforward activities to complicated app development, services like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS work together to offer scalable and adaptable solutions that satisfy a range of customer demands.
5. Data Security Measures
Encryption, firewalls, and compliance procedures safeguard private data, guaranteeing secure data transfer and storage and promoting confidence in cloud-based solutions.
6. Seamless Collaboration
Cloud solutions, which integrate several components for real-time sharing, editing, and secure document and file storage, allow teams to collaborate from any location.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing Components
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud components will increasingly integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve user experiences across sectors by allowing more intelligent data processing and predictive analytics.
2. Edge Computing Expansion
Data processing will be closer to consumers by integrating edge computing and cloud technologies, which will lower latency and enhance real-time capabilities in Internet of Things devices and apps.
3. Serverless Architecture
By eliminating the need to manage servers and enabling developers to concentrate on apps, serverless computing is transforming cloud architecture and accelerating and lowering the cost of cloud adoption.
4. Sustainable Cloud Solutions
Initiatives for green cloud computing will place an emphasis on energy efficiency, minimizing the impact on the environment through data center optimization and the use of renewable energy sources.
5. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Companies will use hybrid and multi-cloud architectures to integrate private and public clouds, improving scalability, security, and flexibility for a range of operational requirements.
6. Quantum Computing Integration
Advances in quantum computing will have an impact on cloud components, providing unmatched processing capacity for intricate problem-solving in fields like artificial intelligence, healthcare, and finance.
Our digital world has changed due to cloud computing, which has made it more efficient, adaptable, and accessible. We can understand how they operate together to power commonplace tools and apps by examining the many components of cloud computing, such as front-end interfaces, back-end systems, and secure networks. In addition to addressing a variety of demands across sectors, these components of cloud computing also guarantee security, scalability, and cooperation. Even further breakthroughs in cloud technology are anticipated in the future because of developments like edge computing and AI integration. It's obvious that in a world that is changing quickly, cloud computing will keep changing the way we store, access, and use data.