What is Cloud Computing and Who Uses Cloud Services?
Explore the realm of cloud computing, a transformative technology that enables users to access and store data, run applications, and deploy services over the internet. Delve into the key players and industries harnessing the power of cloud services for enhanced efficiency, scalability, and collaboration.

Cloud computing is a technical cornerstone that has revolutionized the way we handle data and access services in our modern digital age. This essay explores the fundamentals of cloud computing, revealing its complexities and the wide range of users that can take advantage of its adaptable features.
Significance of Cloud Computing in the Modern Digital Environment
The modern expanding digital environment has made cloud computing a widely accepted concept. Knowing its importance and determining who benefits from its services is crucial in the modern world. As technology develops, comprehending the workings of cloud computing becomes crucial to comprehending the always-changing digital ecosystem.
Cloud Solutions: A Radical Paradigm Shift in Technology
Because conventional computing is not flexible or scalable, it is difficult to adjust to changing needs. Businesses and individuals are turning to cloud computing in search of dynamic alternatives, which are changing data processing, storage, and access ways. Cloud services represent a departure from conventional IT methods because they are dependent on remote servers and provide a more flexible option. In the modern constantly changing electronic countryside, this progression satisfies the growing demand for effective, scalable, and accessible technology solutions.
What exactly is cloud computing, and who are the primary users of cloud services?
Defining Cloud Computing:
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as storage, processing power, and software—over the Internet. Unlike the traditional model of hosting applications and data on local servers, cloud computing relies on remote servers, often maintained by third-party providers.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
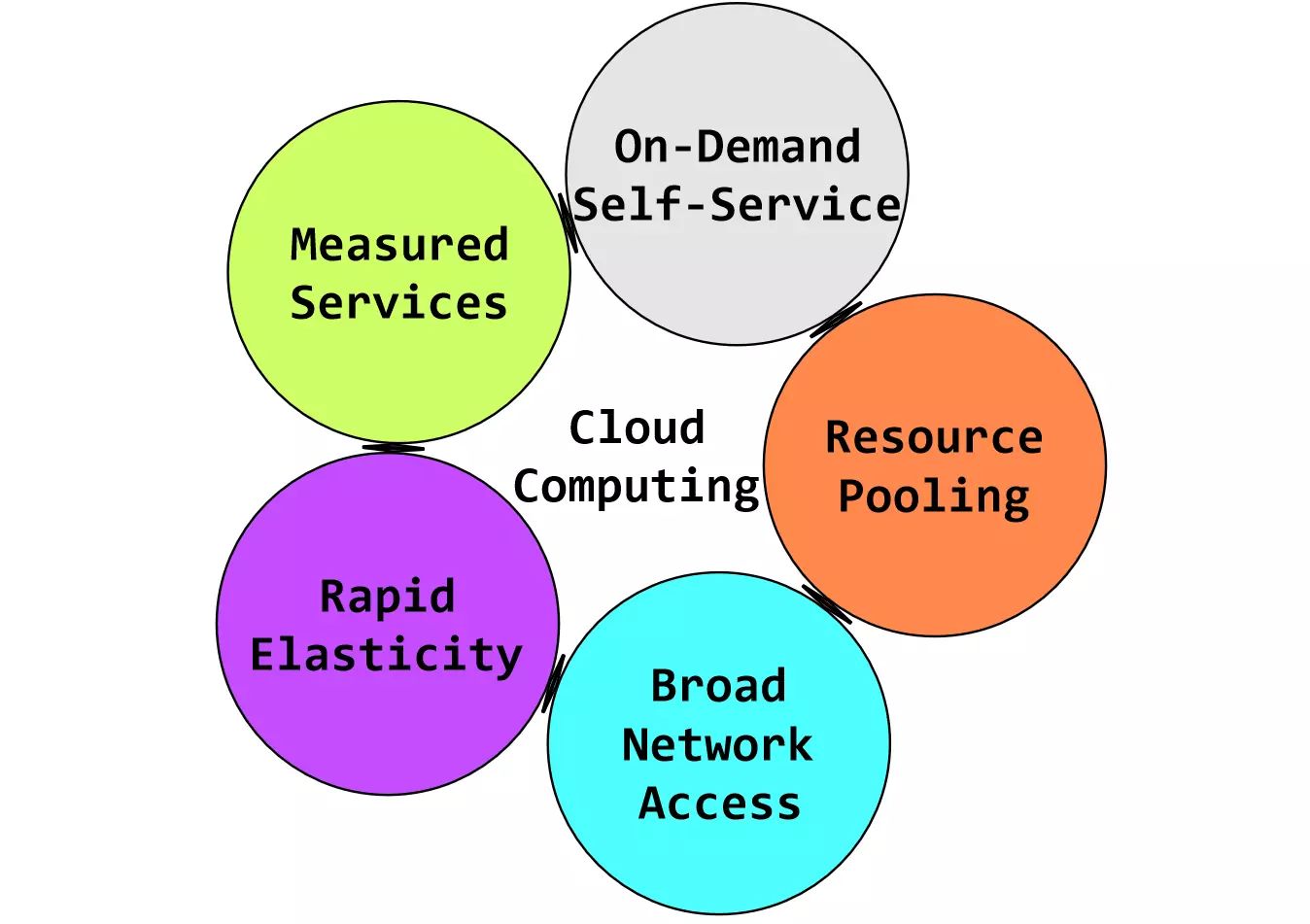
1. On-Demand Service: Users can access resources as needed, paying only for what they use.
2. Scalability: The ability to scale resources up or down based on demand, providing flexibility.
3. Resource Pooling: Resources are shared among multiple users, optimizing efficiency.
4. Broad Network Access: Services are accessible over the internet from various devices.
Who Uses Cloud Services?
1. Businesses of All Sizes:
Startups: Cloud services offer cost-effective solutions, allowing startups to avoid significant upfront infrastructure investments.
SMEs: Small and medium-sized enterprises benefit from scalable resources, adapting to changing business needs.
Large Enterprises: Corporations leverage the cloud for efficiency, data management, and global collaboration.
2. Individuals
Students: Cloud-based tools facilitate collaborative learning and provide access to resources anytime, anywhere.
Freelancers: Cloud services enable freelancers to collaborate with clients, store work securely, and use software without heavy installations.
General Users: Every day consumers use cloud services for storage, email, and entertainment, such as streaming music and videos.
3. Developers
App Development: Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure and services necessary for developing, testing, and deploying applications.
Open Source Collaboration: Developers worldwide collaborate on projects through cloud-based repositories and version control systems.
4. Government and Nonprofit Organizations
Efficiency in Public Services: Governments use cloud computing to enhance services, streamline processes, and store data securely.
Nonprofits: Organizations with limited budgets benefit from the cost-effectiveness and accessibility of cloud solutions.
5. Healthcare Industry
Data Management: Cloud services facilitate secure storage and sharing of medical records, improving patient care.
Research: Cloud computing accelerates medical research by providing computational power for complex analyses.
Types of Cloud Computing
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service offers virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It provides the fundamental building blocks for IT, including virtual machines, storage, and networks. With IaaS, users have the flexibility to manage and control the underlying infrastructure, allowing for a more customizable and scalable computing environment. This type of cloud service is particularly beneficial for businesses that require extensive control over their IT infrastructure without the burden of physical hardware maintenance.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service is a cloud computing model that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the complexity of infrastructure. PaaS offerings typically include development frameworks, databases, and other tools necessary for application development. It streamlines the development process, enabling developers to focus on coding and innovation rather than managing underlying infrastructure details. In many fast-growing tech hubs across the United States, including active digital markets like Tampa, app developers Tampa teams like Halo Digital often rely on PaaS solutions to build applications faster while minimizing hardware and maintenance costs. PaaS is ideal for businesses seeking efficiency in application development and deployment.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and update software locally. SaaS providers host and maintain the software, making it accessible to users through a web browser. This model is prevalent in various applications, including customer relationship management (CRM), email services, and collaboration tools. SaaS is renowned for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, making it a popular choice for both businesses and individuals.
Cloud Categories Based on Deployment Models
1. Public Cloud
The public cloud is like the bustling marketplace of cloud services. In this model, cloud resources, including servers, storage, and applications, are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider. These services are made available to the general public over the Internet. Public clouds offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, as users pay only for the resources they consume. It's an ideal option for businesses with fluctuating workloads and a need for accessibility from various locations.
2. Private Cloud
Contrary to the public cloud, the private cloud is like having a personalized, secure estate. Here, the cloud infrastructure is exclusively used by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. The private cloud provides enhanced control, customization, and security, making it suitable for industries with stringent compliance requirements, such as finance or healthcare. While it may involve higher initial costs, the tailored nature of the private cloud can be a strategic investment for certain enterprises.
3. Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is the Goldilocks of cloud deployment. It's a blend of public and private cloud models, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This approach provides greater flexibility and more deployment options. Businesses can leverage the scalability of the public cloud for non-sensitive operations while keeping critical data and applications in a more controlled private environment. Hybrid clouds are ideal for organizations seeking an optimal balance between cost efficiency and data security.
4. Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud takes things a step further by incorporating services from multiple cloud providers. This model allows businesses to cherry-pick the best features from different providers, preventing vendor lock-in and optimizing performance. It's a strategic approach to avoid relying on a single provider for all cloud services. While managing multiple providers requires careful orchestration, the benefits include improved redundancy, reliability, and the ability to choose services that align precisely with specific business needs.
Cloud computing stands as a transformative force in our digital landscape, reshaping how we store, process, and access data. From startups to healthcare, its adaptable features cater to diverse users. Understanding its significance and the various deployment models, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, illuminates the dynamic choices available. Whether public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud, the cloud revolution continues to redefine our technological horizons.































































