How Does AI Work?
Discover how AI works, from data and machine learning to neural networks and real-world applications, explained in simple, clear language anyone can understand.
In our day-to-day lives, artificial intelligence frequently feels magical. You get a prompt response when you ask a question. By looking at your face, your phone unlocks. Products you might enjoy are suggested by shopping applications. Everything has a fluid, quick, and almost human feel.
As a result, many believe that AI truly has human-like thought processes. But the reality is easier. AI is emotionless, thoughtless, and unaware. It uses data patterns to create intelligent assumptions. It appears that thinking is a quick calculation.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the term used to describe machines that are made to imitate specific features of human intelligence. These systems are capable of decision-making, problem-solving, picture recognition, and language comprehension.
But AI lacks consciousness, feelings, and awareness. In contrast to humans, it does not "understand" things. Rather, it analyzes data and looks for trends in information.
These tasks include:
-
Recognizing images
-
Understanding language
-
Making predictions
-
Solving problems
-
Making decisions
AI is a broad field. Inside it, there are two important subfields:
-
Machine Learning (ML): AI that allows systems to learn from data, identify trends, and enhance performance without the need for human programming.
-
Deep Learning: Layered neural networks are used in this kind of machine learning to handle massive volumes of data and resolve challenging issues.
To understand how AI works, we must begin with data, the foundation behind every smart system, showing the importance of AI in turning raw information into meaningful decisions.
So… How Does AI Actually Work?
Massive datasets are analyzed by AI, which finds patterns, makes adjustments through training, and uses mathematical models to forecast results. Over time, accuracy is continuously increased by repetition and feedback.
1. Data: The Fuel of AI
Large-scale data analysis, pattern recognition, and prediction improvement are how AI systems learn. AI models are incapable of training, adapting, or operating efficiently without high-quality data.
Data can be:
-
Text (books, articles, websites)
-
Images (photos, videos)
-
Audio (voice recordings)
-
Numbers (financial data, sensor readings)
-
User behavior (clicks, searches, purchases)
Consider introducing a child to the concept of a cat. You show them a variety of cats in various colors, sizes, and positions. The toddler eventually picks up on patterns and understands what distinguishes a "cat" from other animals.
AI operates similarly, using mathematical computations in place of intuition and vast datasets in place of experience. To learn efficiently, it begins by looking for patterns after collecting data.
2. Machine Learning: Learning from Patterns
AI systems can learn from data without needing to be specifically built for every scenario due to a process called machine learning.
Here’s a simplified process:
-
Input: Provide data (for example, emails labeled as “spam” or “not spam”).
-
Training: The system analyzes patterns in the data.
-
Model Creation: It builds a mathematical model based on those patterns.
-
Prediction: When given new data, it makes predictions based on what it learned.
For example, in spam detection:
-
The system studies thousands of spam and non-spam emails.
-
It identifies patterns like certain words, links, or formatting.
-
When a new email arrives, it predicts whether it’s spam.
It doesn't fully comprehend the definition of spam. Instead, it accurately classifies fresh messages by identifying patterns and similarities based on previously examined emails.
3. Reinforcement Learning: Learning Through Rewards
Another kind of machine learning is called reinforcement learning, in which artificial intelligence gains knowledge by interacting with its surroundings and getting feedback.
Rather than receiving labeled samples, the machine learns by making mistakes.
The process looks like this:
-
The AI takes action.
-
It receives a reward or penalty.
-
It adjusts its strategy to maximize future rewards.
For example:
-
AI playing chess or video games
-
Robots learning how to walk
-
Systems optimizing traffic signals
Over time, the system improves by learning which actions lead to better outcomes.
Many advanced artificial intelligences combine deep learning and reinforcement learning to learn complicated behaviors, respond to feedback, and make extremely intelligent and optimal decisions.
That brings us to neural networks.
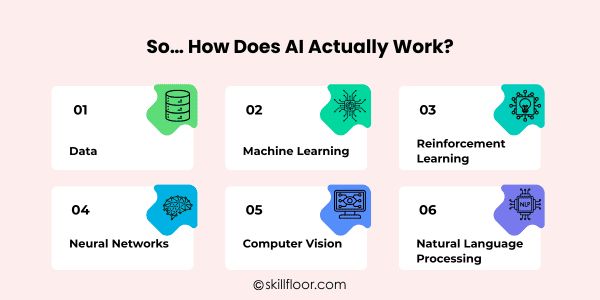
4. Neural Networks: Inspired by the Human Brain
Artificial neural networks, which are computer models modeled after the structure of the human brain and are intended to process data through interconnected layers for complicated pattern recognition, are the foundation of deep learning.
A neural network consists of:
-
An input layer (receives data)
-
One or more hidden layers (process data)
-
An output layer (produces results)
Each connection between nodes has a weight. During training, the system adjusts these weights to reduce errors and improve accuracy.
The more layers a network has, the more complex patterns it can learn. That’s why it’s called “deep” learning.
Neural networks power many of today’s most impressive AI systems.
One major application is Computer Vision.
5. Computer Vision: How AI Sees the World
A subfield of artificial intelligence called computer vision allows robots to simulate human visual comprehension by analyzing, interpreting, and extracting meaningful information from images and videos.
It allows systems to:
-
Recognize faces
-
Detect objects in images
-
Analyze medical scans
-
Power self-driving cars
Millions of labeled photos are used to train computer vision models. Shapes, edges, textures, and object structures are among the patterns they gradually pick up.
For example, in a self-driving car:
-
Cameras capture images of the road.
-
AI detects pedestrians, vehicles, and traffic signs.
-
The system makes driving decisions based on what it “sees.”
But AI doesn’t just understand images.
It can also process human language.
6. Natural Language Processing (NLP): Teaching AI to Understand Language
The goal of the AI area of natural language processing (NLP) is to enable machines to comprehend, interpret, and produce human language.
It powers:
-
Chatbots
-
Voice assistants
-
Translation tools
-
Sentiment analysis systems
NLP effectively analyzes, interprets, and creates human language from text and speech data by combining linguistics, machine learning, and deep learning approaches.
Large Language Models are among the most sophisticated advances in natural language processing (NLP), capable of comprehending context, producing text, and carrying out intricate language tasks.
Types of AI
AI can be categorized into three types:
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
The only type of artificial intelligence that is currently being used in real-world applications is narrow AI, sometimes referred to as weak AI. It cannot function beyond its predetermined limitations or generalize like humans; instead, it is intended to carry out particular tasks like language translation, image recognition, suggestions, or voice help.
It is designed to perform specific tasks such as:
-
Image recognition
-
Language translation
-
Recommendations
-
Chatbots
2. General AI
Strong AI, or general AI, is a theorized type of artificial intelligence that can carry out any intellectual work that a human can. It would be able to reason, solve problems, adapt, and learn on its own in a variety of domains, in contrast to narrow AI. But there are currently no such systems.
Key Characteristics of General AI:
-
Capable of human-like reasoning and understanding
-
Able to transfer knowledge across different tasks
-
Can learn and adapt without task-specific programming
-
Possesses advanced decision-making abilities
-
Remains a theoretical concept under research
3. Superintelligence
Superintelligence is the term used to describe a hypothetical type of artificial intelligence that is superior to human intelligence in all areas, such as creativity, logic, emotional intelligence, and scientific advancement. On a never-before-seen scale, it would surpass humans in problem-solving and decision-making. It is still a theoretical idea that is mostly explored in study and theory, though.
Key Characteristics of Superintelligence:
-
Exceeds human intelligence in all cognitive areas
-
Capable of rapid self-improvement
-
Could solve complex global challenges
-
Raises significant ethical and safety concerns
-
Currently theoretical and not yet developed
Limitations of AI
AI has many drawbacks despite its amazing promise, such as bias, a lack of comprehension, reliance on high-quality data, and the possibility of making mistakes while making decisions.
1. Bias
Artificial intelligence (AI) models may inadvertently replicate or magnify social, cultural, or systemic bias if the data they are learning from contains such bias.
2. No True Understanding
Artificial intelligence (AI) does not have awareness, emotions, or true cognition; instead, it analyzes data patterns instead of comprehending meaning in the same manner that people do.
3. Errors and Hallucinations
Because language models rely on probability patterns rather than validated facts or real-time truth validation processes, they may produce inaccurate or fake information.
4. High Resource Usage
Large AI models require a lot of processing power, sophisticated gear, and energy to train and run, which raises infrastructure and environmental issues.
5. Data Dependency
The amount and quality of training data have a major impact on AI performance; inadequate, out-of-date, or subpar data can drastically lower accuracy and dependability.
6. Limited Generalization
Unlike humans, the majority of AI systems are task-specific and suffer outside of their training scope, which prevents them from adapting flexibly to novel situations.
Understanding these constraints enables people and organizations to utilize AI responsibly, guaranteeing its ethical application, cautious supervision, enhanced data practices, and reasonable expectations regarding its capabilities.
Real-World Applications of AI
AI is quickly changing industries all over the world by increasing productivity, facilitating creative solutions in a variety of fields, automating jobs, and improving decision-making.
1. Healthcare
-
Disease detection
-
Medical imaging analysis
-
Drug discovery
2. Finance
-
Fraud detection
-
Risk assessment
-
Algorithmic trading
3. Education
-
Personalized learning
-
AI tutoring systems
4. Marketing
-
Customer behavior analysis
-
Content generation
-
Predictive analytics
5. Transportation
-
Autonomous vehicles
-
Traffic optimization
6. Retail & E-commerce
-
Product recommendations
-
Inventory management
-
Demand forecasting
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a far-off, futuristic idea; rather, it has permeated every aspect of daily life, impacting our ability to communicate, work, shop, travel, and make decisions.
The Future of AI
AI is still developing quickly due to improvements in processing power, data accessibility, and innovative research. AI systems are anticipated to grow in capability, accessibility, and integration with common tools and international industries as technology develops.
In the coming years, we may see:
-
More collaboration between humans and AI
-
Automation of repetitive and time-consuming tasks
-
Smarter and more context-aware personal assistants
-
Greater emphasis on ethical and responsible AI development
-
Increased integration of AI in healthcare and scientific research
-
More advanced AI-powered cybersecurity systems
AI is more likely to enhance human abilities, improve decision-making, increase productivity, and transform daily operations within individuals and organizations rather than completely replace humans.
The real impact of AI systems will depend on how responsibly they are developed and implemented as they become more advanced and widely accessible. By prioritizing ethics, transparency, and human involvement, society can maximize the potential benefits of AI while minimizing risks and ensuring sustainable progress in the long term.
AI does not possess a mind of its own, nor is it magic. It is an effective technique based on data, patterns, and astute math. The mystery disappears, and the opportunity is evident once you fully comprehend how AI works. Instead of seeing robots taking over, you see technology that can help you think more clearly, work more quickly, and make better decisions. It's important to think differently. Not just engineers will have a place in the future. Those who know how to use these instruments properly will own them. AI is meant to support your creativity, not to replace it. Learn it, challenge it, and make meaningful use of it. That's how you maintain your humanity and stay ahead.































































