What is Pay-Per-Click Advertising?
Learn what Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising is, how it works, its benefits, and how to get started with campaigns to boost your business’s online presence.

When I first heard about Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, I was surprised at how effective it could be for businesses of all sizes. I’ve seen PPC campaigns help small startups grow into successful companies. But I’ve also seen campaigns fail when they weren’t managed properly, wasting money with little result.
So, what is PPC, and why do so many people talk about it in digital marketing? Let me explain it in a simple way so you can understand it easily and use it yourself.
Why Businesses Need PPC Advertising
One of the biggest challenges businesses face today is getting noticed in a crowded marketplace. With so many competitors vying for attention, it can be tough to stand out. Traditional advertising methods like billboards or TV spots are expensive and often don’t target the right audience. Even with digital marketing, organic search engine optimization (SEO) takes time to deliver results.
So, how do businesses quickly and effectively reach their target audience online? This is where PPC advertising steps in.
What Is Pay-Per-Click Advertising?
PPC advertising is an online marketing strategy where advertisers pay a fee each time someone clicks on their ad. Instead of trying to "earn" visits organically, PPC allows you to buy traffic to your website. It’s essentially a way to purchase visits, but the beauty lies in how targeted and measurable it can be.
For example, when you search for “best laptops under $1000,” you might see ads at the top of the search results page. These ads are PPC campaigns. The advertisers behind them only pay when someone clicks on their ad, ensuring their budget is spent on actual interest rather than mere impressions.
The most common platform for PPC advertising is Google Ads, but it also includes options like Bing Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn Ads.
How Does PPC Work?
At its core, PPC works on a bidding system combined with relevance factors. Let me walk you through it:
1. The Auction Process
When you create a PPC ad, you select specific keywords that you want your ad to show for. When someone searches for those keywords, an auction happens behind the scenes. Google (or another platform) decides which ads to show and in what order based on factors like:
-
Maximum Bid: How much you're willing to pay for a click.
-
Quality Score: A metric that evaluates your ad's relevance, landing page quality, and expected click-through rate (CTR).
The goal is to balance relevance and bid to provide the best user experience.
2. Cost-Per-Click (CPC)
Your actual cost per click is often less than your maximum bid because of the auction dynamics. For example, if you bid $2.00 but the second-highest bidder only bids $1.50, you might only pay $1.51 for the click.
3. Ad Placement
Ads with higher relevance and bids are more likely to appear in prime positions, such as the top of the search results. This ensures that high-quality ads (not just high-budget ones) get the spotlight.
Why PPC Works
PPC is effective because it combines immediacy, measurability, and precision targeting. But let's dive deeper into its advantages.
1. Immediate Results
Unlike SEO, which can take months to improve your ranking, PPC delivers instant visibility. As soon as your campaign is live, your ads can appear in front of potential customers searching for your product or service.
2. Highly Targeted
With PPC, you can specify exactly who sees your ads based on factors like:
-
Demographics: Age, gender, income level.
-
Location: Local, national, or international targeting.
-
Interests and Behaviors: Recent search history, online activity.
This ensures that your ads reach the people most likely to convert.
3. Budget Control
You have full control over how much you spend. Whether your budget is $10 a day or $10,000, PPC allows you to set limits and adjust spending as needed.
4. Measurable Metrics
Platforms like Google Ads provide detailed analytics, including:
-
Impressions (how often your ad is shown).
-
Click-through rate (CTR).
-
Conversions (sales, sign-ups, etc.).
This data allows you to refine your strategy and maximize ROI.
Types of PPC Ads
Pay-per-click advertising offers a variety of ad types to cater to different business goals and audience preferences. Each format has its unique strengths, and understanding these can help you design a well-rounded PPC strategy. Let’s explore the options, including Demand Generation (DemandGen) ads, a newer entrant gaining traction.
1. Search Ads
These are text-based ads that appear on search engine results pages (SERPs) when users enter specific queries. They are ideal for targeting users who are actively searching for products or services. For example, if someone searches “affordable web design services,” your ad can appear at the top of the results if you’re bidding on relevant keywords.
-
Best For: High-intent customers looking for specific solutions.
2. Display Ads
Display ads are visually engaging and appear on websites within the Google Display Network or other advertising networks. They often include banners, images, or rich media and are excellent for building brand awareness.
-
Best For: Reaching a broad audience, retargeting past visitors, or introducing your brand to potential customers.
3. Shopping Ads
These ads are designed for e-commerce businesses, showcasing individual products directly within search results. They often include product images, prices, and ratings. Shopping ads help users make quick purchasing decisions by offering detailed product information upfront.
-
Best For: Driving online retail sales for tangible goods.
4. Video Ads
Video ads, commonly seen on platforms like YouTube, use engaging content to capture attention. These ads can appear before, during, or after video content and are great for storytelling or demonstrating products and services.
-
Best For: Increasing brand engagement and awareness through dynamic, memorable visuals.
5. Social Media Ads
Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and TikTok allow you to create PPC campaigns tailored to specific demographics and interests. Social PPC leverages user data to deliver highly targeted ads within social feeds, stories, or video content.
-
Best For: Building community engagement, driving traffic, or generating leads in social spaces.
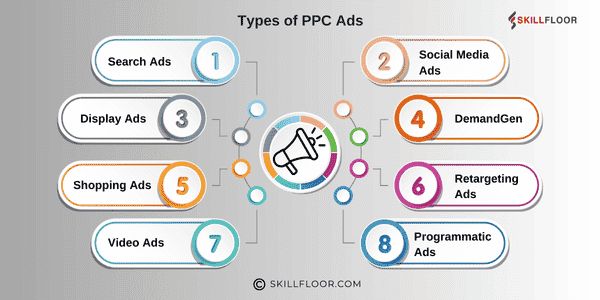
6. Demand Generation (DemandGen) Ads
DemandGen ads are a newer, advanced PPC format designed to go beyond intent-based marketing. Unlike traditional PPC formats, which focus on immediate clicks or conversions, DemandGen ads aim to create demand by targeting audiences who might not yet know they need your product or service. They leverage rich audience insights and appear across channels like YouTube, Gmail, and Discovery networks.
-
How They Work: These ads use visually engaging formats like carousel images or immersive multimedia to inspire potential customers. They encourage users to explore your brand without necessarily having an immediate search intent.
-
Best For: Generating awareness and interest at the top of the funnel, nurturing potential leads over time.
7. Remarketing/Retargeting Ads
These ads target users who have previously interacted with your website or app but didn’t convert. By reminding them of your offerings, remarketing ads help re-engage potential customers and encourage them to complete their journey.
-
Best For: Boosting conversions by reconnecting with warm leads.
8. Programmatic Ads
Programmatic advertising uses AI and machine learning to automate ad placements across multiple platforms. It’s data-driven and allows for hyper-targeted campaigns with real-time optimization.
-
Best For: Large-scale campaigns requiring precise targeting and efficient budget allocation.
By incorporating a mix of these PPC ad types, including the innovative DemandGen ads, you can create a well-rounded strategy that addresses every stage of the customer journey, from awareness to conversion. Each type serves a specific purpose, so aligning your ad formats with your campaign goals is the key to success.
How to Get Started with PPC
If you're new to PPC, starting can feel overwhelming. Here's a step-by-step guide to ease you into it:
1. Define Your Goals
What do you want to achieve? Is it more website traffic, lead generation, or sales? Having a clear objective will shape your strategy.
2. Conduct Keyword Research
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to find relevant keywords. Look for terms with high search volume and manageable competition.
3. Set a Budget
Decide how much you’re willing to spend daily or monthly. Remember, PPC allows you to scale up or down as needed.
4. Create Ad Copy and Creatives
Write compelling headlines and descriptions. For display ads, invest in high-quality visuals that grab attention.
5. Target Your Audience
Use demographic, geographic, and behavioral targeting to refine who sees your ads.
6. Monitor and Optimize
Once your campaign is live, regularly review performance metrics. Adjust bids, update ad copy, and test new strategies to improve results.

Challenges to Watch Out For
While PPC offers numerous benefits, it’s not without its challenges:
1. High Competition
For competitive keywords, CPC can skyrocket, especially in industries like legal, insurance, or real estate.
2. Click Fraud
Sometimes, competitors or bots may click on your ads maliciously, wasting your budget. Most platforms have systems in place to minimize this risk.
3. Complexity
PPC platforms can be intimidating for beginners. Mismanaged campaigns can lead to wasted spend with little return.
4. Requires Continuous Monitoring
Unlike some marketing strategies, PPC isn’t “set it and forget it.” Regular adjustments are needed to stay effective.
Real-World Examples
To put it into perspective, let me share a couple of scenarios where PPC made a difference:
-
E-commerce Store: A small online retailer used shopping ads to highlight their products directly on search results. Within three months, they doubled their sales by reaching high-intent shoppers.
-
Local Business: A local bakery used PPC to target users within a 10-mile radius. They ran a campaign promoting their weekend specials, leading to a 30% increase in foot traffic.
PPC Best Practices
To make the most of your PPC efforts, here are some best practices I’ve found invaluable:
-
Use Negative Keywords: Exclude irrelevant terms to avoid wasting money on unqualified clicks.
-
Test and Optimize: Continuously experiment with different ad copy, creatives, and targeting to see what works best.
-
Align Ads with Landing Pages: Ensure your landing page delivers on the promise of the ad to improve conversion rates.
-
Track Conversions: Use tools like Google Analytics to measure success and fine-tune your campaigns.
PPC vs. Other Advertising Models
It’s also worth noting how PPC stacks up against other advertising methods:
-
PPC vs. CPM (Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions): CPM focuses on visibility, making it better for brand awareness, while PPC emphasizes actions (clicks).
-
PPC vs. CPA (Cost-Per-Acquisition): CPA charges you only for completed actions, such as a purchase, making it more result-oriented but often more expensive.
Pay-per-click advertising is a dynamic and versatile tool for businesses looking to grow their online presence. While it requires careful planning and management, the rewards can be substantial when done right. From my experience, PPC isn’t just about throwing money at ads—it’s about understanding your audience, setting clear goals, and continuously refining your approach.
If you’re considering PPC, take the plunge but start small, monitor closely, and learn as you go. It might just be the game-changer your business needs.































































