What is Blockchain Technology? How Does Blockchain Work?
Explore the fundamentals of Blockchain technology and gain insights into its workings. Understand the decentralized and secure nature of Blockchain, unraveling its potential impact on various industries.

Blockchain has become one of the most important ideas in the ever-changing field of technology. It is a breakthrough paradigm in data management and security, far from being just a catchphrase. In contrast to traditional systems, blockchain's decentralized architecture improves security and builds trust by doing away with the need for a central authority. Its rising popularity indicates a radical change in the way we understand and handle digital data, and it portends more transparent and safe data handling in the future.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that securely records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain ensures transparency, trust, and security by storing data in blocks that link together cryptographically. Each block contains a list of transactions and a reference to the previous block, making it resistant to tampering. This technology goes beyond cryptocurrencies, finding applications in various industries for transparent and trustworthy record-keeping.
The Fundamentals of Security in Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed, decentralized ledger technology that makes record-keeping safe and open. As opposed to conventional databases, which are managed by a single entity and are centralized, blockchains function through a network of computers called nodes. Every node in the network is equipped with a copy of the whole blockchain, and they cooperate to verify and log transactions.
Using Decentralized Security to Reduce Single Points of Failure
To understand why Blockchain emerged as a solution, let's explore the complications it addresses.
In centralized systems, a single point of failure exists. If the central authority is compromised, the entire system is vulnerable to hacking, fraud, and data manipulation. Blockchain resolves this issue by distributing the control across multiple nodes, making it extremely difficult for any single entity to manipulate the data.
Additionally, trust is a significant challenge in online transactions. Parties involved often rely on intermediaries like banks or payment processors to facilitate trust. Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries by providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions, fostering trust in a trustless environment.
How does Blockchain work?
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network where data is stored in blocks, linked through cryptographic hashes. Consensus mechanisms ensure agreement among nodes, creating a secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant ledger.
Let's break down the workings of Blockchain step by step.
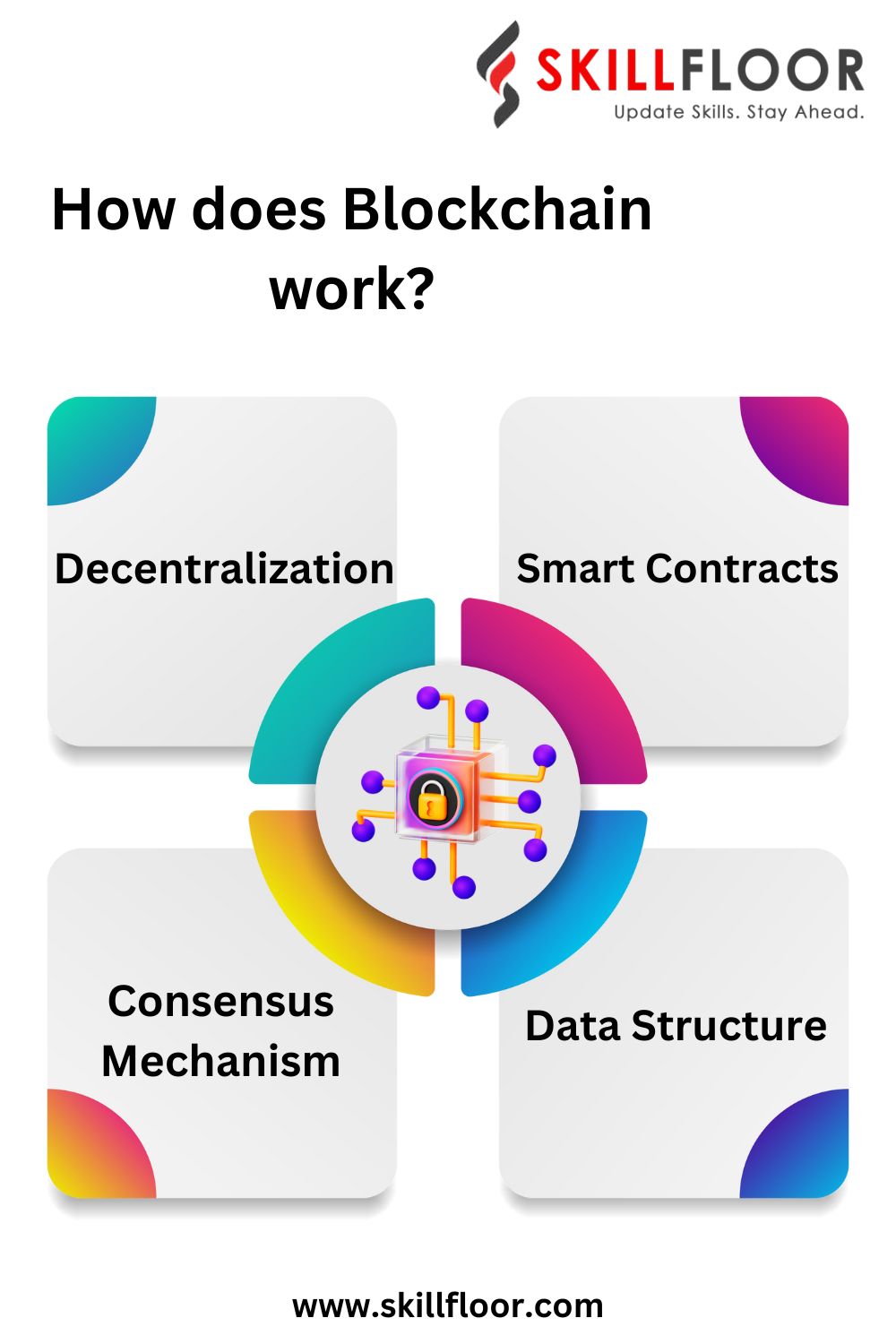
1. Data Structure: Blocks
Blockchain gets its name from its structure, which consists of a chain of blocks. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block, forming a chronological chain of records.
2. Decentralization
As mentioned earlier, a blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes. These nodes work collaboratively to validate and agree on the state of the blockchain. When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcast to the network, and the nodes validate its authenticity through a consensus algorithm.
3. Consensus Mechanism
Consensus mechanisms ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions. The most common consensus mechanism is Proof of Work (PoW), where nodes compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add a new block to the chain. Another mechanism, Proof of Stake (PoS), assigns the right to validate transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency a participant holds.
4. Immutability and Security
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chain of interlinked blocks. Changing the information in a block would require recalculating the hash for that block and all subsequent blocks, which is computationally infeasible.
This immutability, combined with decentralization and consensus mechanisms, enhances the security of the blockchain, making it resistant to fraud and tampering.
5. Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology extends beyond simple transactional records. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are a powerful feature of certain blockchain platforms. These contracts automate and enforce the execution of contractual agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
6. Use Cases
Blockchain technology finds applications in various industries beyond cryptocurrencies. It is employed in supply chain management, healthcare, finance, and more. For instance, in supply chain management, blockchain ensures transparency by providing a tamper-proof record of the journey of products from manufacturer to consumer.
Why is Blockchain Popular?
Blockchain's popularity stems from its revolutionary approach to data management. Its decentralized and tamper-resistant nature addresses critical issues in traditional systems, offering enhanced security and transparency. The elimination of intermediaries in transactions, facilitated by smart contracts, reduces costs and increases efficiency. The immutability of blockchain ensures the integrity of records, making it resistant to fraud. As industries recognize these advantages, the popularity of blockchain extends beyond cryptocurrencies to diverse applications like supply chain, healthcare, and finance, showcasing its potential to reshape how we interact with and trust digital information.
Structure and Design of Blockchain
Blockchain, the technological marvel underpinning cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is more than just a decentralized ledger; it is a sophisticated system with a carefully crafted structure. In this segment, we'll unravel the intricate design of blockchain and explore the elements that make it a resilient and revolutionary technology.
1. The Foundation: Blocks
At the core of blockchain architecture lies the concept of blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block, forming a chain. This chronological structure ensures the integrity and transparency of the data.
2. Decentralization: Nodes and Networks
Blockchain operates on a network of nodes, each maintaining a copy of the entire blockchain. The decentralized nature of these nodes eliminates the reliance on a single central authority, distributing the control across the network. This not only enhances security but also prevents a single point of failure.
3. Consensus Mechanisms: Ensuring Agreement
To maintain the integrity of the blockchain, consensus mechanisms play a pivotal role. Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are popular mechanisms ensuring that nodes agree on the validity of transactions before adding them to the blockchain. PoW involves solving complex mathematical puzzles, while PoS assigns validation rights based on the amount of cryptocurrency held.
4. Immutability: The Inalterable Chain
Once a block is added to the blockchain, changing its content becomes practically impossible. The immutability of the blockchain arises from the cryptographic hash of each block, linking it to the previous one. Any attempt to alter a block would necessitate recalculating the hash for that block and all subsequent blocks a computationally infeasible task.
5. Smart Contracts: Code-Based Automation
Blockchain's versatility extends beyond transactions with the inclusion of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts, coded with the terms of the agreement, automate and enforce contractual obligations without the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts have found applications in diverse fields, from finance to supply chain management.
6. Public and Private Blockchains: Tailoring Security and Access
Blockchain networks can be categorized into public and private. Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone, offering transparency and inclusivity. On the other hand, private blockchains restrict access to a specific group, providing enhanced control over participants. The choice between public and private blockchains depends on the desired level of transparency and security.
7. Scalability Challenges: Tackling Growth Pains
Despite its merits, blockchain faces scalability challenges. As the number of transactions grows, scalability becomes a concern. Various solutions, such as sharding and layer 2 scaling solutions, are being explored to address these challenges and ensure that blockchain technology can handle increased transaction volumes without compromising efficiency.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized architecture and tamper-resistant design, is reshaping how we manage, secure, and trust digital data. Beyond cryptocurrencies, its applications in various industries underscore its transformative potential. As Blockchain continues to evolve, addressing scalability challenges and refining its structure, it stands as a beacon of innovation, offering a more secure, transparent, and efficient future for digital interactions.






























































