What are the Objectives of Cyber Security
Don't let cyber threats put you at risk! Learn the key objectives of cybersecurity to protect your data, networks, and systems from growing online dangers.

In the current world, almost everything we do depends on technology whether it’s shopping online, working remotely, or connecting with family and friends. But with all these digital conveniences comes a big challenge: cyberattacks. As a cybersecurity expert, I have seen how fast these threats are growing, and why it’s so important for everyone to understand the Objectives of Cyber Security. The truth is, protecting our personal information and systems isn’t just about keeping hackers out; it’s about making sure our data stays safe, our systems are up and running, and our digital lives remain secure. Did you know that cyberattacks surged by 75% in 2024, with businesses facing over 1,800 attacks every week? This growing number of attacks is a serious reminder of just how essential strong cybersecurity really is.
The Objectives of Cyber Security are about much more than stopping hackers they focus on ensuring your data stays private, accurate, and always available when you need it. These core principles confidentiality, integrity, and availability are the foundation of cybersecurity. They help us protect sensitive information, keep systems working smoothly, and ensure that nothing is tampered with. For example, phishing attacks have increased by 1,265% over the last year, showing how important it is to stay protected. By understanding the Objectives of Cyber Security, you can be better prepared to defend against these threats and create a safer online world for yourself and those around you.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect systems, networks, and data from cyberattacks or unauthorized access. In simpler terms, it’s the digital defense that keeps your personal and organizational information safe from hackers, criminals, and other threats in the online world. With everything becoming more digital from banking and shopping to social media and cloud storage the need for cybersecurity has never been greater. Just like you lock your doors to protect your home from intruders, cybersecurity is about locking the doors of your digital world to protect your information and online activities. One of the key objectives of cybersecurity awareness is to help individuals and organizations understand these risks and take the necessary precautions.
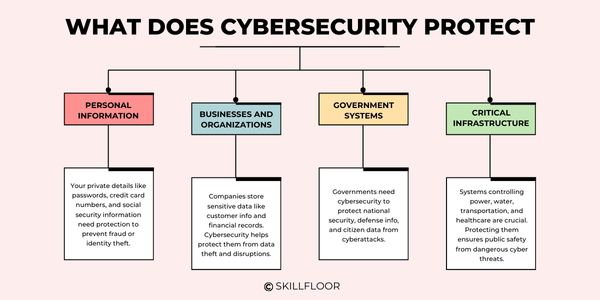
What Does Cybersecurity Protect?
Importance of Cybersecurity for protecting various aspects of our digital world:
-
Personal Information: This includes your private details, like social security numbers, credit card information, and passwords. If your personal data is exposed or stolen, it can lead to fraud, identity theft, or financial loss. One of the main objectives of cybersecurity awareness is to ensure individuals recognize the value of safeguarding their personal data.
-
Businesses and Organizations: Companies store sensitive data such as financial records, customer details, and proprietary information. Cybersecurity helps protect businesses from cybercriminals who might try to steal this information or disrupt operations.
-
Government Systems: Cybersecurity is also critical for governments to protect national security, sensitive defense information, and citizen data from cyberattacks or espionage.
-
Critical Infrastructure: This includes systems that control essential services like electricity, water, transportation, and healthcare. Attacks on these systems can have severe consequences on public safety, emphasizing why raising cybersecurity awareness is essential to prevent such threats.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
There are several types of cyber threats that cybersecurity aims to protect against:
-
Malware: This is a general term for malicious software, such as viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware, that is designed to damage or disrupt systems. Malware can steal data, lock users out of their devices, or cause damage to files and systems.
-
Phishing: Phishing involves tricking individuals into giving away personal information, like usernames, passwords, or credit card numbers, often through fake emails or websites that appear to be legitimate. For instance, you might get an email that looks like it's from your bank, asking you to update your account information, but it's actually a scam.
-
Hacking: Hackers are individuals or groups who attempt to break into systems or networks to steal, manipulate, or destroy data. They might exploit vulnerabilities in software or use weak passwords to gain access.
-
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: A DoS attack floods a server with more traffic than it can handle, causing it to crash and become unavailable. This can disrupt websites, applications, and services.
-
Ransomware: This type of malware locks users out of their devices or encrypts their data, demanding a ransom payment in exchange for restoring access. It's a growing problem for both individuals and organizations.
-
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks (MitM): In this attack, cybercriminals intercept and manipulate communications between two parties, often to steal sensitive information or inject malicious code into websites.
The Fundamental Objectives of Cyber Security
Protecting Confidentiality
Confidentiality means that sensitive data is kept private and only accessible to authorized people or systems. This could be anything from your personal information (like Social Security numbers and medical records) to a company’s trade secrets. Keeping this information secure prevents it from falling into the wrong hands, which could lead to identity theft, financial loss, or even reputational damage.
Confidentiality is ensured through several key methods:
-
Encryption: Encryption is like putting a padlock on your data. When information is encrypted, it is transformed into unreadable code that can only be unlocked with a specific key. For instance, when you make an online purchase, your credit card details are encrypted, making it nearly impossible for hackers to access them.
-
Authentication and Authorization: Only authorized users should be able to access certain data. Authentication ensures that users are who they say they are (through methods like usernames, passwords, or biometrics), while authorization determines whether they can access specific information.
Without confidentiality, your personal data could be leaked, causing everything from financial theft to personal harm. For example, a bank that fails to protect its customers’ financial data could face lawsuits, fines, and a significant loss of trust.
Ensuring Integrity
Integrity is about making sure data stays accurate and unaltered unless there is an authorized change. Think about the data you rely on daily, like your bank balance, medical records, or financial reports. If someone changes that data without permission, it can lead to serious consequences.
Integrity is maintained by:
-
Hashing: This is a process that takes data (like a password or message) and converts it into a fixed-length string of characters. Even a small change in the original data will cause a dramatic difference in the output, making it easier to detect any tampering. This way, we can check if data has been altered.
-
Checksums and Digital Signatures: Checksums are used to verify that data hasn't been altered, and digital signatures are like “signed” proof that the data was sent by an authorized source and hasn’t been changed along the way.
For example, if a hacker changes the data in a company’s financial report to cover up fraudulent activity, the integrity of the report would be compromised, potentially leading to legal and financial consequences.
Ensuring Availability
Availability ensures that systems, data, and resources are available when needed. Imagine being unable to access your email, bank account, or work files during an important meeting or at a crucial time. That’s where availability becomes essential.
To guarantee availability:
-
Backup Systems: These are redundant systems that take over in case the primary system fails. For example, if your computer crashes, a backup system ensures you can restore your work without data loss.
-
Disaster Recovery Plans: These plans ensure that in the event of a cyberattack, natural disaster, or hardware failure, your systems can be restored quickly and efficiently. A business continuity plan might involve automatic system restoration or accessing cloud-based backups.
-
Load Balancing: This spreads traffic evenly across servers to prevent any single server from getting overwhelmed. For instance, during a big sale on an e-commerce website, load balancing can ensure that the website remains functional even when many people are browsing at once.
If availability is compromised, it could lead to prolonged outages, customer dissatisfaction, or loss of business. For example, if an online service goes down for hours during peak business hours, customers may seek competitors’ services.
Other Key Objectives of Cyber Security
While confidentiality, integrity, and availability are the primary objectives, there are other essential elements that cybersecurity addresses.
Authentication and Identity Management
Authentication helps confirm that someone is who they say they are. It’s essential for preventing unauthorized access to systems and data. Identity management includes managing and verifying user identities and controlling access to specific resources.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires two or more forms of verification to grant access. This can include something you know (a password), something you have (a phone or security token), or something you are (a fingerprint or facial recognition). For example, if you log into your bank account online, you might enter your password and then receive a code on your phone to confirm your identity.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO allows users to log in once and access multiple services without having to repeatedly enter passwords. For instance, if you log into your work account, you can automatically access your email, cloud storage, and other applications without logging in again.
Without proper authentication, unauthorized users could easily gain access to sensitive systems or data. For example, if someone were to guess your password and gain access to your email account, they could misuse it or steal important information.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Even the best preventative measures can’t stop every cyberattack. That’s why continuous monitoring of systems is crucial. Monitoring helps organizations detect unusual activities or early signs of an attack.
Incident response refers to how a business reacts when a breach happens. A well-prepared incident response team can quickly isolate the problem, reduce damage, and restore operations as soon as possible.
For example, if a hacker gains unauthorized access to a system, the incident response team can quickly identify the breach, shut down the affected systems, and investigate how the attack happened. They may then work on restoring data from backups, fixing the vulnerability, and informing the affected parties.
Risk Management
Risk management in cybersecurity involves identifying potential threats, assessing the severity of those threats, and deciding how to reduce or eliminate them. By understanding which risks are most likely to affect systems, businesses can take steps to prevent them.
For example, a company might identify that employees using personal devices to access company data increases the risk of malware or a data breach. The company could then invest in a secure virtual private network (VPN) or restrict access to sensitive systems from non-company devices.
Good risk management helps organizations allocate resources where they are needed most, ensuring that they are better prepared for potential threats. By assessing risks regularly, businesses can stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Organizations must adhere to various legal and regulatory requirements to protect customer data and privacy. These laws ensure that businesses are responsible in how they manage sensitive information.
For example:
-
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): GDPR is a regulation in the European Union that ensures personal data is handled with care and gives individuals more control over their data. A company must obtain consent before collecting personal data, and if there’s a breach, the company must inform affected individuals within a certain time frame.
-
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): HIPAA requires healthcare organizations to safeguard personal health information and to ensure that it’s only accessed by authorized personnel.
Failure to comply with these regulations could lead to heavy fines, legal consequences, and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Protecting Endpoints
Endpoints are devices like laptops, smartphones, tablets, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices that connect to networks. Attackers often target these devices because they provide a direct way into a network. Protecting these endpoints is important for keeping the entire system secure.
To protect endpoints:
-
Antivirus Software: This software helps detect and prevent malware from infecting devices. It constantly scans files and programs for malicious behavior and removes any threats it finds.
-
Firewalls: Firewalls act as barriers between your device and the internet, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. They help protect against malicious traffic and unauthorized access.
-
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools continuously monitor endpoints for unusual behavior, helping detect attacks early and respond to threats before they can spread.
If an endpoint is compromised, hackers can potentially gain access to an entire network, making it important to secure all devices. For example, if an employee’s laptop is infected with malware, it could spread throughout the organization’s network, causing widespread damage.
The Evolution of Cyber Security Objectives
As technology continues to evolve, so do the cybersecurity threats. What worked in the past might not be enough to protect against modern threats. The rise of cloud computing, IoT devices, and artificial intelligence (AI) has made cybersecurity more complex. The rise of mobile technology, for example, has made it even harder to secure systems because employees are working from various locations and devices.
At the same time, cybersecurity measures are evolving. AI and machine learning are now being used to detect threats more quickly by analyzing large volumes of data to identify unusual patterns. Cloud security solutions are also more advanced, helping organizations secure data stored in the cloud while ensuring it remains available and accessible.
Challenges in Achieving Cyber Security Objectives
- Evolving Nature of Threats
Cyber threats are constantly changing. Hackers are always coming up with new techniques and tools to break into systems. For example, ransomware attacks have become more sophisticated and harder to detect, often using encryption to hold data hostage until a ransom is paid.
-
Complexity of IT Infrastructure
Businesses today use a wide range of technologies: cloud services, mobile devices, remote workforces, and third-party services. This makes securing everything much more challenging. Without proper planning and management, it's easy for systems to become vulnerable.
-
Human Error
Human error continues to be one of the biggest challenges in cybersecurity. People may forget to update software, click on phishing emails, or use weak passwords. Since people are often the weakest link in security, it's essential to provide ongoing training and awareness programs to help employees avoid making these mistakes.
-
Resource Limitations
Cybersecurity requires a significant investment of time, money, and resources. Small businesses or startups may not have the same resources as large enterprises to build robust security systems. However, even small businesses can take basic steps like using strong passwords, installing antivirus software, and educating employees on security best practices.
The main objective of cybersecurity is to protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, damage, or theft. It aims to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information by preventing cyber threats like hacking, malware, and phishing. Cybersecurity also helps in safeguarding sensitive data, maintaining privacy, and ensuring the smooth operation of systems and networks. In simple terms, its goal is to keep digital environments safe from harmful activities and protect both individuals and organizations from potential risks.































































