The Role of Data Scientists: Skills and Responsibilities
Explore the role of data scientists, their key and essential skills and responsibilities, and how mastering data can boost your career and future opportunities.

We live in a world where data overflows. Information is produced with each click, search, purchase, and online activity. These days, companies make decisions based on insights gleaned from all the data in their environment rather than relying solely on conjecture.
Consider Amazon proposing items you might like or Netflix suggesting what to watch next. Data scientists, experts who utilize data science to transform unstructured, raw data into insightful knowledge that helps businesses make better decisions and enhances the lives of millions of people, are the brains behind these intelligent systems.
Who Is a Data Scientist?
An expert who gathers, examines, and understands complicated data to assist organizations in making defensible decisions is known as a data scientist. They tackle real-world problems by combining their understanding of business, statistics, mathematics, and programming.
As opposed to a data engineer who constructs data infrastructure or a data analyst who focuses largely on interpreting data that already exists, a data scientist works at the nexus of both, evaluating data and creating predictive models that inform future choices.
In simple terms:
-
Data Analysts concentrate on comprehending historical events by data analysis, trend identification, and result summarization to clarify what truly transpired.
-
Data Scientists proceed further by forecasting future events and elucidating their causes utilizing models and insights.
-
Data Engineers create, construct, and manage the infrastructure and systems that enable effective data collection, archiving, and analysis.
Data scientists are extremely significant and in great demand across a wide range of businesses due to their unique blend of strong technical skills and keen analytical thinking, which enables them to offer insightful information.
Core Responsibilities of a Data Scientist
To fully understand the role of data scientists, we must examine their daily activities. Their tasks typically follow a lifecycle, ranging from the impact on the company to the raw data.
1. Data Collection and Cleaning
Data rarely comes in a perfect format. It may be incomplete, inconsistent, or scattered across different systems.
A data scientist:
-
Gathers data from databases, APIs, or external sources
-
Cleans missing or incorrect values
-
Transforms raw data into usable formats
-
Ensures data quality and reliability
In fact, a lot of experts claim that preparing and cleaning data takes up between 60 and 70 percent of a data scientist's work. Even the most sophisticated model will not work without clean data.
2. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Data preparation is followed by exploratory data analysis (EDA). In order to successfully direct additional investigation, it entails analyzing and visualizing data to find patterns, trends, and anomalies.
Exploratory Data Analysis involves:
-
Identifying patterns and correlations
-
Detecting anomalies or outliers
-
Creating visualizations
-
Forming hypotheses
Data scientists use summary statistics, charts, and graphs to reveal hidden narratives in the data. The course of the entire project is often decided by this step.
3. Building Machine Learning Models
Many people associate data science with the stage of building machine learning models, when algorithms are used to analyze data to generate classifications, forecasts, and significant patterns for decision-making.
Data scientists use algorithms to:
-
Predict customer behavior
-
Detect fraud
-
Classify emails as spam
-
Forecast sales
-
Recommend products
Depending on the problem, they may use:
-
Regression models
-
Classification models
-
Clustering techniques
-
Neural networks
For example, companies like Google use machine learning models to improve search results and deliver relevant advertisements.
4. Model Evaluation and Optimization
Making a model is only one aspect of model evaluation and optimization. It needs to be tested, validated, and improved by data scientists to guarantee correctness, dependability, and efficient real-world performance.
Data scientists:
-
Measure accuracy, precision, and recall
-
Validate models using test datasets
-
Tune hyperparameters
-
Prevent overfitting
This guarantees that, given the right conditions for data preparation and quality, the model will function well and align with key data science objectives, performing accurately on both historical data and in real-world situations.
5. Deployment and Monitoring
Following development and testing, a model needs to be implemented into actual systems and continuously evaluated for correctness, dependability, and performance.
Data scientists:
-
Collaborate with engineers to integrate models into applications
-
Monitor performance and detect model drift
-
Update models when data or business needs change
-
Ensure reliability and scalability of solutions
Through the implementation and monitoring of models in practical settings, data scientists guarantee that insights are implemented efficiently, providing tangible business benefits and continuously facilitating more intelligent, data-driven choices.
6. Communicating Insights
Effective communication, which entails clearly discussing findings, results, and suggestions with all pertinent stakeholders, is one of the most neglected yet essential duties of a data scientist.
A data scientist must:
-
Translate complex findings into simple language
-
Create dashboards and visual reports
-
Present insights to non-technical stakeholders
-
Recommend data-driven actions
Clear explanation is crucial for well-informed, data-driven business decisions since even the most advanced model is useless if decision-makers are unable to understand its implications, insights, or value.
Essential Skills of a Data Scientist
After learning what data scientists do, let's examine the skills needed to carry out these duties efficiently.
1. Technical Skills
a. Programming Skills
Programming is fundamental in data science. Popular languages include:
-
Python
-
R
-
SQL
Python is widely used because of its powerful libraries for data manipulation and machine learning.
b. Statistics and Mathematics
Data science is built on mathematical foundations. Professionals must understand:
-
Probability theory
-
Linear algebra
-
Calculus
-
Statistical inference
These concepts allow data scientists to interpret results accurately and design effective models.
c. Machine Learning and AI
Understanding algorithms is critical. This includes:
-
Supervised learning
-
Unsupervised learning
-
Deep learning basics
-
Model evaluation techniques
Frameworks such as TensorFlow and Scikit-learn are commonly used for implementation.
d. Data Visualization Tools
Communicating insights requires visualization skills. Tools include:
-
Tableau
-
Power BI
-
Matplotlib
-
Seaborn
Visualization transforms complex data into clear, compelling stories.
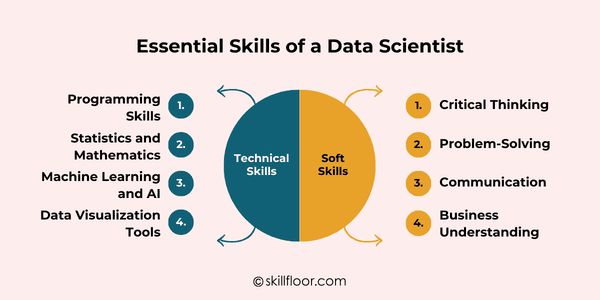
2. Soft Skills
A successful data scientist is not defined solely by technical proficiency. Soft skills are just as vital.
a. Critical Thinking
Data scientists must challenge presumptions, closely study trends, and rationally look at problems in order to find the underlying causes and significant insights.
b. Problem-Solving
Uncertainty is a common characteristic of business difficulties. Data scientists are required to transform ambiguous inquiries into well-defined, feasible assignments that can be efficiently examined and resolved.
c. Communication
Giving concise answers, having confidence, and being able to simplify complex facts are necessary when sharing insights with CEOs, marketing teams, or product managers.
d. Business Understanding
Data scientists may create models and analyses that add value and are in line with broader business plans by having a thorough understanding of the aims and objectives of the organization.
Must-Have Tools and Technologies Every Data Scientist Should Know
1. Programming & Data Analysis Tools
Languages like R and Python are crucial. R focuses on statistical analysis and visualization, but Python is flexible for data processing and machine learning.
2. Machine Learning Libraries
Building models is made quicker and simpler by libraries like TensorFlow and Scikit-learn. TensorFlow is excellent for deep learning applications, while Scikit-learn performs well for generic machine learning workloads.
3. Data Visualization Tools
Results may be effectively communicated with the aid of tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Matplotlib. Interactive dashboards are provided by Tableau and Power BI, while Matplotlib enables intricate, adaptable Python visuals.
4. Big Data Platforms
Frameworks like Apache Spark and Hadoop are necessary for managing large datasets. Hadoop offers dependable distributed storage and computation, whereas Spark is quick and adaptable for processing on a big scale.
5. Cloud Computing Services
Data scientists can concentrate on analysis rather than infrastructure thanks to platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure, which offer scalable storage, processing capacity, and pre-built data science applications.
6. Collaboration & Notebook Tools
Data scientists may create, test, and share code and visualizations with teams using tools like Google Colab and Jupyter Notebook.
Industries That Hire Data Scientists
Data scientists are in demand across many different sectors:
-
Healthcare: Use data to refine treatment strategies, forecast illness patterns, and enhance patient outcomes.
-
Finance: Identifying fraud, evaluating risks, and encouraging wiser investing choices.
-
E-commerce: Enhancing sales tactics, evaluating consumer behavior, and developing recommendation systems.
-
Marketing: Improving audience targeting, assessing campaign efficacy, and customer segmentation.
-
Technology: Creating machine learning apps, AI solutions, and software system enhancements.
-
Retail: Predicting demand, controlling inventory, and giving clients a customized purchasing experience.
Data science is crucial for businesses like Google, Netflix, and Amazon to improve user experience and spur innovation.
How to Become a Data Scientist
If you aspire to become a data scientist, here are practical steps to follow:
1. Build a Strong Foundation
Start with the fundamentals by learning programming, statistics, and maths. These abilities are the foundation of all data science activity.
2. Learn Tools and Technologies
To get ready for real-world tasks, get practical expertise with Python, SQL, R, and well-known machine learning packages.
3. Take a Data Science Course
Enroll in a structured data science course to experience industry-standard tools and methodologies, guided learning, and hands-on exercises.
4. Work on Real Projects
Create a portfolio using real-world datasets. Engage in contests on websites such as Kaggle to hone your abilities and display your work.
5. Gain Practical Experience
Internships and entry-level jobs enable you to work with teams, comprehend business issues, and put your skills to use in practical situations.
6. Keep Learning
The field of data science is changing quickly. Growth requires ongoing education through additional classes, certificates, research, and keeping up with trends.
Challenges Faced by Data Scientists
Despite its allure, data scientists face a number of obstacles that they must carefully overcome:
1. Poor Data Quality
Data that is disorganized, inconsistent, or incomplete can hinder projects, lower accuracy, and taint analysis. Data cleaning frequently requires a lot of time.
2. Ambiguous Business Questions
Stakeholders could pose ambiguous queries such as "How can we increase revenue?" Accurate analysis is necessary to convert these into quantifiable, useful measurements.
3. Model Deployment
Making a model is just half of the task. It is frequently necessary to work with the IT and engineering teams to integrate it into production systems.
4. Rapidly Evolving Tools
Technologies and tools used in data science evolve rapidly. Remaining effective requires keeping up with the most recent libraries, frameworks, and platforms.
5. Data Privacy and Compliance
GDPR, HIPAA, and other privacy rules and regulations, as well as industry-specific compliance standards, must be followed while handling sensitive data.
6. Communicating Insights Effectively
If outcomes are not easily comprehensible to stakeholders who are not technical, even the most precise model is worthless for making well-informed decisions.
Real-World Case Study in Data Science
A case study from the real world demonstrates how data science is used to address important business issues. It illustrates the entire procedure, from data collection to the provision of useful insights that inform choices.
Take, for instance, an online retailer trying to increase consumer purchases. Customer purchase data is initially collected and cleaned by data scientists. They create prediction algorithms, segment their consumer base, and evaluate trends to suggest products that each user is most likely to purchase.
The model is put into the recommendation system, its accuracy is checked, and its performance is regularly tracked. Better customer involvement, more individualized experiences, and higher sales are the outcomes for the business.
The Future of Data Science
Data science is a field that is always changing and has a bright future. Automation, machine learning, and artificial intelligence developments will influence how businesses gather, process, and utilize data.
Predictive analytics, real-time decision-making, and ethical AI will become more and more important to data scientists. Professionals will have more time for strategic problem-solving and innovation if repetitive duties are automated.
Industries across healthcare, finance, retail, and technology will continue to rely on data science to drive efficiency, improve customer experiences, and create new products and services.
With the rapid evolution of tools, algorithms, and processes, the future also necessitates ongoing learning. Those who adapt and combine technical expertise with business insight will thrive in this data-driven world.
Being a data scientist is an interesting and fulfilling career path. From finding hidden patterns in jumbled data to developing insights that actually have an impact, there are fresh hurdles every day. The finest aspect? You get to link numbers to practical choices that benefit people and businesses alike. Anyone can succeed in this industry if they are curious, persistent, and eager to learn. The job of a data scientist involves more than just arithmetic and code; it involves transforming data into possibilities, solutions, and narratives that influence the future. The first step is where your effect begins.






























































